|
Alcedo semitorquata
(Half-collared kingfisher)
Blouvisvanger [Afrikaans]; Isaxwila (generic term for
kingfisher) [Xhosa]; isiXula [Zulu]; Muningi (generic term for kingfisher)
[Kwangali]; Mavungana, N'waripetani, Xitserere [Tsonga]; Mmatlhapi, SeinŰdi
(generic terms for kingfisher) [Tswana]; Kobaltijsvogel [Dutch]; Martin-pÍcheur
ŗ demi-collier [French]; Kobalteisvogel [German]; Pica-peixe-de-colar
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves (birds) > Order: Coraciiformes
> Family: Alcedinidae
The Half-collared kingfisher is widespread but uncommon, with
populations scattered across sub-Saharan Africa. In southern Africa, it is most
common in Zimbabwe and South Africa's rivers, streams and estuaries. Its diet
consists mostly of fish, which it hunts by sitting on a perch for long periods
then, once it spots a fish, diving in to catch it. It nests in burrows dug into
vertical riverbanks, excavated by both sexes. Here it lays 1-6, usually 3-4 eggs
which are incubated by both sexes. The chicks probably remain in the nest for
about 27 days, learning to fly soon after emerging.
Distribution and habitat
Widespread but uncommon,
with populations scattered across sub-Saharan Africa. In southern Africa it
occurs in northern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip), eastern Botswana,
northern Zimbabwe, central and northern Mozambique and eastern and southern
South Africa. It generally prefers narrow rivers, streams and estuaries with
dense vegetation onshore, but it may also move into coastal lagoons and lakes.
|
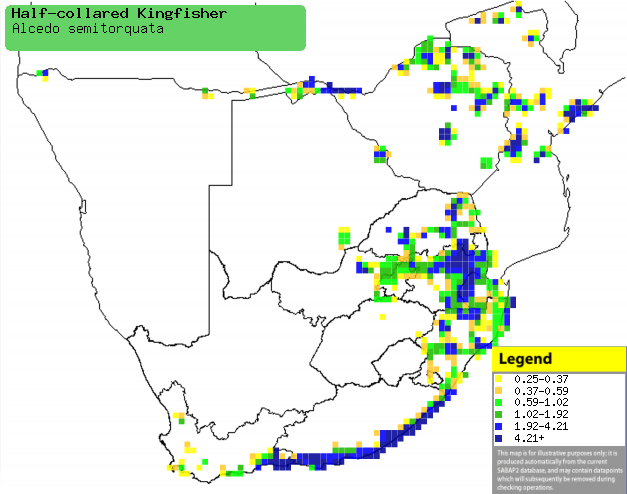 |
|
Distribution of Half-collared kingfisher in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
Its diet consists mostly of
fish, which it hunts by sitting on a perch for long periods then, once it spots
a fish, diving in to catch it. The following food items have been recorded in
its diet:
- small fish
- Tilapia (Oreochromis alcalicus)
- Robbers (Brycinus)
- Barbs (Barbus)
- aquatic insects
- small amphibians
Breeding
- It nests in burrows dug into vertical
riverbanks, excavated by both sexes. The entrance is usually wider than it
is high, and is often concealed by overhanging vegetation.
- Egg-laying season is from July-March, usually peaking from
September-October.
- It lays 1-6, usually 3-4 eggs which are incubated by both sexes, usually taking alternating 1-2 hour shifts.
- The chicks probably remain in the nest for about 27 days, learning to
fly soon after leaving.
Threats
Not threatened, although deforestation is a serious concern,
as it has damaged populations in KwaZulu-Natal.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
