Ardea purpurea (Purple heron)
Rooireier [Afrikaans]; Ucofuza, Undofu
[Xhosa]; Samunkoma gomugeha [Kwangali]; Kokolofitoe -lalatšehla [South Sotho];
Rikolwa [Tsonga]; Kôkôlôhutwę [Tswana]; Purperreiger [Dutch]; Héron
pourpré [French]; Purpurreiher [German]; Garça-vermelha [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Ciconiiformes
> Family: Ardeidae
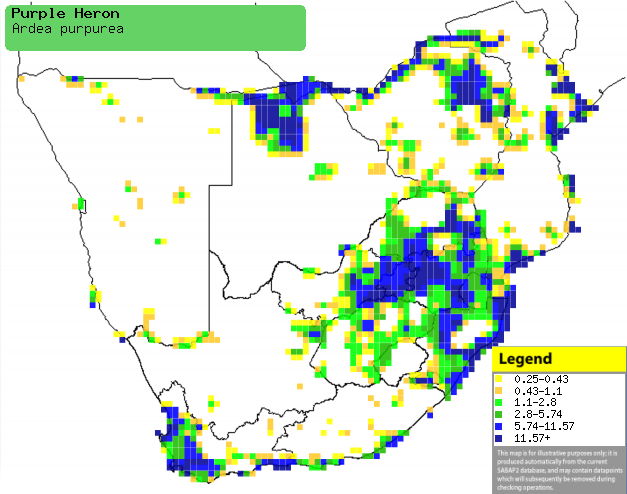
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from western Europe to southern China and Indonesia,
also occupying Madagascar and sub-Saharan Africa. In southern Africa, it is uncommon to locally common in
northern Botswana, the Caprivi Strip (Namibia), northern Zimbabwe, central and
southern Mozambique and South Africa. It generally prefers dense vegetation (especially Phragmites
reedbeds) on the edge of shallow wetlands or mangroves; it is less tolerant
of disturbed habitats than the Grey heron.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Purple heron in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
- Predators of eggs and sometimes chicks
Movements and migrations
Resident in perennial wetlands, although it may
make nomadic movements to exploit temporary wetlands.
Food
It mainly eats fish, doing most of its foraging in reedbeds,
slowly wading through floating vegetation before rapidly stabbing its prey. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Vertebrates
- fish
- Clarias (catfish)
- Labeo altivelis (Manyane labeo)
- Labeo cylindricus (Redeye labeo)
- Oreochromis machrochir (Greenhead tilapia)
- Tilapia rendalli (Redbreast tilapia)
- Brycinus imberi (Imberi)
- amphibians
- reptiles
- small mammals
- birds
- Invertebrates
Breeding
- Monogamous and territorial, usually breeding small colonies in dense
reedbeds or stands of trees (occasionally along with other species), rarely
nesting solitarily. It defends its nest against intruders by performing a
variety of displays and sometimes attacking, stabbing with its bill.
- The nest (see image below) is built by both sexes, consisting of a
platform of bent Phragmites reeds or Bulrushes (Typha capensis),
lined with reed leaves and small water plants. It is typically placed over
water in a reedbed; the male chooses the site where the nest is built.
 |
|
| Purple heron sitting on nest with chick. [photo Peter Steyn ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking from July-February.
- It lays 2-5 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 25-27
days.
- Competition for food between the chicks is intense, sometimes resulting
in the death of the youngest sibling. They leave the nest at about 20 days
old, fledging 10-15 days later and becoming fully independent at
approximately 55-65 days old.
Threats
Not threatened, although it is probably negatively impacted
by wetland drainage and agriculture.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
