|
Tockus erythrorhynchus
(Red-billed hornbill)
RooibekneushoringvoŽl [Afrikaans]; umKholwane (also
applied to Crowned hornbill) [Zulu]; Rukoko (generic term for hornbills with red
or yellow bills) [Kwangali]; Goto, Hoto (generic names for hornbill) [Shona];
Umkhotfo (generic term for hornbill) [Swazi]; Nkorho (generic term for smaller
hornbills) [Tsonga]; KŰrwÍ [Tswana]; Roodsnaveltok [Dutch]; Calao ŗ bec rouge
[French]; Rotschnabeltoko [German]; Calau-de-bico-vermelho [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Bucerotiformes > Family: Bucerotidae
 |
 |
| Red-billed hornbill, Krugersdorp
Nature Reserve, South Africa. [photo Gerhard Theron
©] |
Red-billed hornbill with dragonfly. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
The Red-billed hornbill occurs from south-eastern Angola and Zambia to southern Africa, where it is common in open,
wooded savanna with sparse ground cover. It feeds mainly on small insects, such
as beetles, ants, termites and flies, but it also eats larger arthropods, small
vertebrates, small seeds and fruit. It nests in natural cavities in trees 0.3-9
m above ground, which the female seals with her own faeces. It lays 2-7 eggs,
which are incubated solely by the female, for 23-25 days. The chicks stay in the
nest for 39-50 days, remaining near the nest for a few more days before joining
their parents in foraging.
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from south-eastern Angola
and Zambia to southern Africa. Within Southern Africa it is common in
north-eastern Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe and north-eastern South Africa. It
generally prefers open, wooded savanna with sparse ground cover.
|
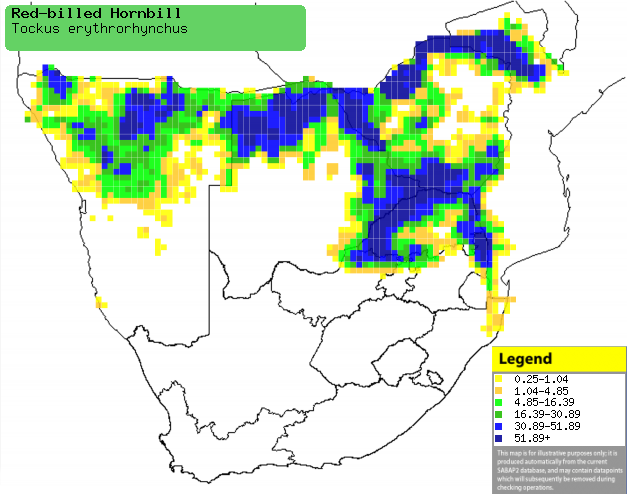 |
|
Distribution of Red-billed hornbill in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
Food
It feeds mainly on small insects, such
as beetles, ants, termites and flies, but it also eats larger arthropods, small
vertebrates, small seeds and fruits. It does most of its foraging on the ground,
rarely hawking prey aerially. The following food items have been recorded in its
diet:
- Animals
- invertebrates
- small vertebrates
- reptiles
- bird eggs and nestlings
- scavenged rodents
- Seeds and fruit
- Boscia (shepherds-trees)
- Commiphora (corkwoods)
Breeding
- It nests in natural cavities in trees 0.3-9.0 m above
ground. The female seals it with her own faeces, leaving a small entrance
hole 3-4 cm wide.
 |
|
|
Red-billed hornbill at its nest, Phabeni Gate,
Kruger Park, South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season after good summer rains, from September-March, peaking
from October-December.
- It lays 2-7, usually 3-5 eggs, as the number depends on rainfall and food
availability before laying.
- Incubation is done solely by the female for about 23-25 days, starting
with the first laid egg.
- The chicks stay in the nest for 39-50 days, remaining near the nest for
a few more days before joining their parents on foraging trips.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact widespread and common.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
