|
Apalis thoracica (Bar-throated apalis)
Bandkeelkleinjantjie [Afrikaans]; Ugxakhweni
[Xhosa]; uMabhelwane [Zulu]; N'walanga, Xinyamukhwarani (generic
terms for apalis) [Tsonga]; halsbandapalis [Dutch]; Apalis à collier
[French]; Halsband-feinsänger [German]; Apalis-de-coleira
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Cisticolidae
> Genus: Apalis
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in patches from Tanzania through Malawi and Zambia
to southern Africa. Here it is common across much of Zimbabwe, central
Mozambique, south-eastern Botswana and South Africa, preferring evergreen
forest, valley bushveld, woodland along drainage lines in the Karoo and scrub
around sand dunes. It is occasionally found in grassland and alien tree stands
and plantations.
|
 |
|
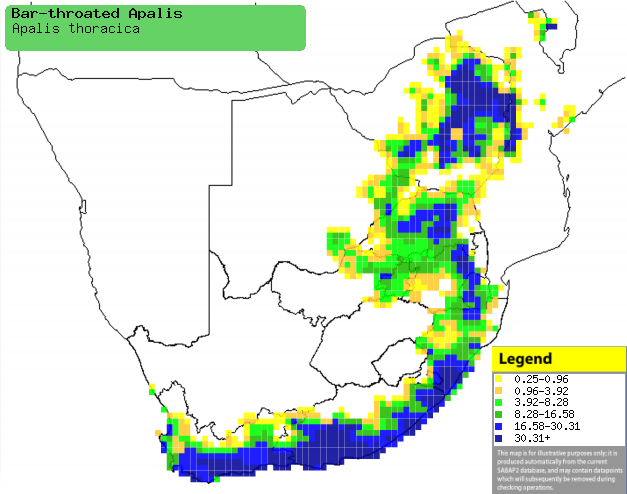
Distribution of Bar-throated apalis in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Klaas's cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats invertebrates gleaned from leaves and twigs,
supplemented with fruit. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Carpels (part of the flower) of Rhincanthis gracilis (Dainty
spurs)
- Fruit of Eriobotrya japonica (Loquat)
Breeding
- The nest is an oval ball with a side entrance, built of fine grass, moss,
lichens and rootlets, secured with spider web. It is typically placed in the
foliage of shrub, sapling or creeper, often 1-3 metres above ground.
- Egg-laying season is mainly from August-March, peaking from
November-December.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 14-18
days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 13-18
days, after which they are still dependent on their parents for food for
some time.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
