|
Cisticola tinniens (Levaillant's
cisticola)
Vleitinktinkie [Afrikaans]; Imvila, Umvila [Xhosa];
Motintinyane (generic term for cisticolas and prinias) [South Sotho]; Timba
(generic name for cisticolas and warblers) [Shona]; Matinti (generic term for
cisticola) [Tsonga]; Vallei-graszanger [Dutch]; Cisticole à sonnette [French];
Uferzistensänger [German]; Fuinha-zunidora [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Cisticolidae
> Genus: Cisticola
 |
 |
|
Levaillant's cisticola. [photo H. Robertson, Iziko ©] |
Levaillant's cisticola, Bot River, South Africa. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
It has populations scattered across Africa south of the
Sahel, from Kenya to Zambia, Angola and southern Africa. Here it is locally
common in marshy vegetation along watercourses, edges of reedbeds, moist
grassland and croplands in the Karoo.
|
 |
|
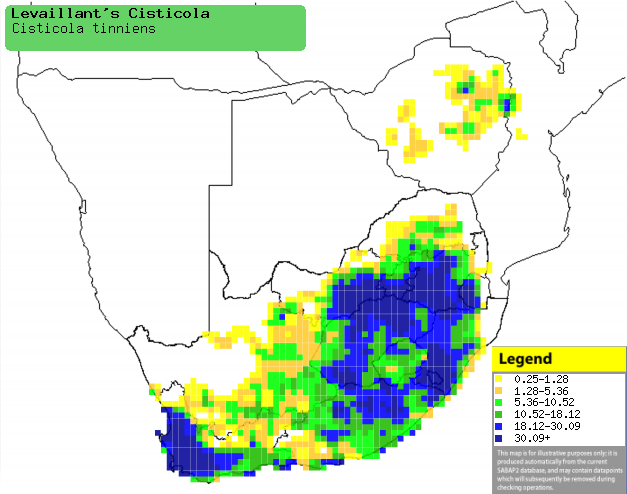
Distribution of Levaillant's cisticola in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Brown-backed honeyguide.
Food
It mainly eats small insects, doing most of its foraging
low down in the undergrowth. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- The nest is an oval or ball shape with a side entrance, built of dry grass
secured with spider web and typically placed near the ground or water, often
in a grass tuft or bush overhanging a stream. A thick lining of plant down
is added to the interior by the female during incubation, who may also
create a kind of "doormat" of soft material below the entrance.
- Egg-laying season is from September-May, peaking from November-March.
- It lays 2-5 eggs, which are incubated for about 11-14 days.
- Not much is known about the chick's development, other than that they
leave the nest after about 14-15 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
