|
Dendrocygna bicolor (Fulvous
duck)
Fluiteend [Afrikaans]; Idada (generic term for duck)
[Xhosa]; Dada, Sekwe (both are generic names for duck or goose) [Shona]; Sekwa
(generic term for duck or goose) [Tsonga]; Sehudi (generic term for duck)
[Tswana]; Rosse fluiteend [Dutch]; Dendrocygne fauve [French]; Gelbe baumente
[German]; Pato-assobiador-arruivado [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Anseriformes >
Family: Dendrocygnidae
This golden-brown coloured duck with long legs and neck
and greyish-black bill is widely distributed worldwide, occurring in the Americas, Africa, Madagascar and
Asia. It is found mainly on large, shallow, inland water bodies with
aquatic plants round the perimeter. Eats pondweed (Potamogeton)
shoots, seeds of aquatic plants, and to a lesser extent, aquatic insects.
Distribution and habitat
Widely distributed worldwide: occurs in tropical South
America, southern North America, Africa, Madagascar and S Asia. Widely
distributed in Africa: occurs in most regions but not equatorial rain forest,
desert and fynbos. In southern Africa, concentrated mainly in Gauteng, Free
State, KwaZulu-Natal, Swaziland, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, N Botswana and Namibia
(mainly in the north). Found mainly on large, shallow, inland water bodies with
aquatic grasses and other aquatic plants around the perimeter.
|
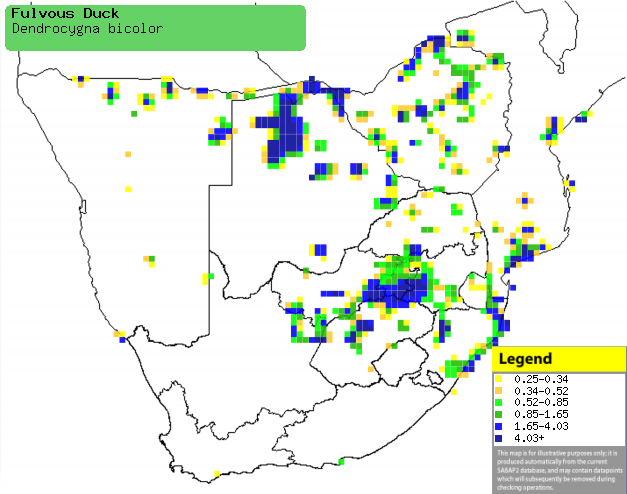 |
|
Distribution of Fulvous duck in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
- Ectoparasites
- Phthiraptera (lice)
- Holomenopon leucoxanthum
- Trinoton aculeatum
- Acidoproctus rostratus
- Worm parasites
- Pathogens
- tuberculosis
- cyathostomiasis
Food
Feeds by dabbling or diving. The records below are based on records from southern Africa, summarised in
Hockey et al. (2005).
- Eats mainly plant matter
- Potamogetonaceae
- Potamogeton crispus (Wavy-leaved
pondweed): eats the shoots. On the Pongola River flood plain in
KwaZulu-Natal, 98.8% of the winter-spring diet consisted of this
plant (aquatic insects formed the remainder of the diet)
- Poaceae (grasses). Eat the seeds of the following
species:
- Echinochloa stagnina (Long-awned water
grass)
- Digitaria ciliaris (Tropical finger
grass)
- Sorghum bicolor (Common wild sorghum)
- Vossia cuspidata (Hippo grass)
- Persicaria
- Polygonum
- Oryza sativa (Cultivated rice)
- Oryza barthii (Wild rice)
- Paspilidium geminatum (Swamp grass)
- Asteraceae (daisy family)
- Ambrosia artemisifolia (Ragweed): eats
seeds and fruit
- Nymphaeaceae (water lilies)
- Nymphaea nouchali (Blue water lily):
including seeds
- Menyanthaceae
- Nymphoides indica (Small yellow water
lily): eats seeds/fruits
- Najadaceae
- Najas horrida (Saw-weed): eats seeds and
fruits of this aquatic plant
- Typhaceae
- Typha domingensis (Bulrush): eats seeds.
- Euphorbiaceae
- Acalypha segetalis (Bushy pondweed):
eats seeds/fruits.
- Algae
- Also aquatic insects.
Breeding
- Nest is built by both sexes and consists of a scrape in
the ground, lined with grass stems, leaves and reeds, and hidden in long
grass within 50 m of water. Makes a more substantial, built-up nest if the
site chosen is on marshy ground near the water's edge. Also known to nest up
to 0.5 m above the water in thick reeds.
- Breeding season (laying dates). Known to nest at
virtually any time of year but generally after good rains.
- The female lays 6-13 eggs (probably laying at most one
egg per day) after which she and her partner take turns in incubating them
for 24-32 days before they hatch. The male usually incubates them at night.
- By 52 days the young are able to fly and by 60 days old
they have almost complete juvenile plumage.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact distribution and density has
expanded as a result of the construction of artificial water bodies (e.g. farm
dams).
Links
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
