|
Larus cirrocephalus
(Grey-headed gull)
Gryskopmeeu [Afrikaans]; Grijskopmeeuw [Dutch]; Mouette à
tête grise [French]; Graukopfmöwe [German]; Gaivota-de-cabeça-cinzenta
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Charadriiformes
> Family: Laridae > Genus: Larus
 |
 |
| Grey-headed gull in breeding plumage,
Paarl Bird Sanctuary, South Africa. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Grey-headed gull in breeding plumage, Paarl Bird
Sanctuary, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
 |
 |
| Grey-headed gull in non-breeding
plumage, Strandfontein Sewage Works, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Grey-headed gull in non-breeding plumage, Paarl
Bird Sanctuary, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in South America and sub-Saharan Africa, with two
separate populations in the continent, one in west Africa and the other
extending from Sudan and Ethiopia south through Uganda, Tanzania, eastern DRC,
Zambia and Angola to southern Africa. Within southern Africa it is fairly common in western and
northern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip), northern Botswana, north-western
Zimbabwe, eastern Mozambique and central and southern South Africa. It generally
prefers coastal islands, estuaries, lagoons, harbours, pans, dams, fresh and
alkaline lakes, large rivers and sewage ponds.
|
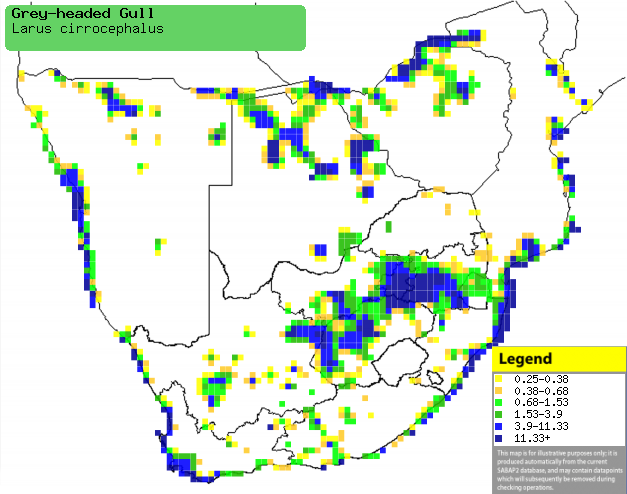 |
|
Distribution of Grey-headed gull in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Resident and sedentary when breeding but often
travelling widely in the non-breeding season.
Food
Like most gulls it is a highly opportunistic feeder, mainly
eating aquatic invertebrates as well as a variety of small vertebrates. It does
most of its foraging in flocks over water, plucking prey from the surface or moving
to rubbish dumps and picnic sites to feed on food scraps. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Vertebrates
- fish
- Sardinops sagax (Sardines)
- cichlids
- frogs
- eggs and chicks of other birds
Breeding
- Monogamous, colonial nester, breeding in colonies ranging from a few to
several hundred pairs spaced 1-4 metres apart, often fighting with other
each other in defence of their territories. It may also join mixed-species
colonies along with Kelp gulls,
Hartlaub's gulls,
Caspian terns,
Swift terns and/or Goliath
herons.
- The nest (see image below) is a a shallow bowl of grass, twigs and weeds
often adjacent to a grass tuft or some other plant. It may also use the old
nest of a Red-knobbed coot or alternatively build a floating platform of
lily leaves and sedges.
 |
|
|
Grey-headed gull nest with eggs, Kamfer's Dam,
Kimberley, South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is mainly from July-October in Botswana and Zimbabwe,
May-June in Gauteng and from February-November in KwaZulu-Natal.
- It lays 1-3 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes starting from the
first egg.
- The chicks flee the nest if disturbed and can run freely within a day of
hatching, while their parents may attack intruders (such as humans) if they
get to close.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
