|
Batis capensis (Cape batis)
Kaapse bosbontrokkie [Afrikaans]; Ingedle, Unongedle
[Xhosa]; uDokotela, umNqube [Zulu]; Bruinflank-vliegenvanger [Dutch]; Pririt du
Cap [French]; Kapschnäpper [German]; Batis do Cabo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Malaconotidae
 |
 |
|
Cape batis male, Kirstenbosch Botanical Gardens,
Western Cape, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Cape batis female, Harold Porter Botanical
Gardens, Western Cape, South Africa. [photo Duncan Robertson ©]. |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Tanzania, Zambia and Malawi to southern Africa.
Here it is locally common in eastern Zimbabwe bordering on Mozambique,
south-central Zimbabwe, Limpopo Province, KwaZulu-Natal, Eastern Cape and
Western Cape. Highly adaptable, it occupies a wide range of habitats, such as
Afromontane and Evergreen forest, closed woodland, valley bushveld, Acacia
woodland along watercourses, plantations, orchards and gardens.
|
 |
|
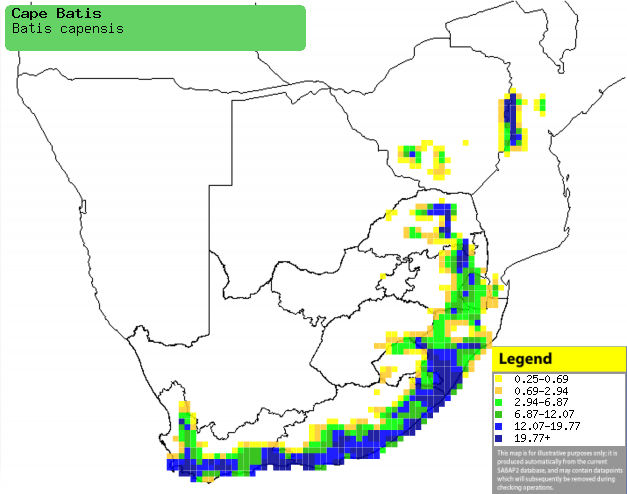
Distribution of Cape batis in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Klaas's cuckoo.
Food
It eats a variety of insect prey, doing most of its
foraging in the lower branches of trees or bushes, gleaning prey from leaves or
bark. The following food items have been recorded in its diet:
Breeding
- Both sexes construct the nest (see image below), which is a small,
thickly-walled cup, made of dry plant material bound together by spider web,
lined with fine plant detritus or hair. It is usually placed on a horizontal
branch of small shrub, about 1-9, usually 3 metres above ground. Nests
aren't usually concealed by vegetation, but they are often difficult to find
due to very dark lighting conditions.
 |
|
Cape batis male (left) and female (right) at their
nest. [photo Peter Steyn ©] |
- Egg-laying season is from August-January, peaking from October-December.
- It lays 1-3 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female, for about
17-21 days with the male bringing her food.
- The chicks are mainly brooded by the female, who feeds them and herself
with food provided by the male. They are brooded and fed at greater
intervals as they get older, until eventually they leave the nest at about
16 days old.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
