|
Merops persicus (Blue-cheeked
bee-eater)
Blouwangbyvreter [Afrikaans]; isiThwelathwela [Zulu];
Sitembandayi (generic term for non-Carmine bee-eaters) [Kwangali]; Muhladzanhu,
Muhlagambu (generic terms for bee-eater) [Tsonga]; Groene bijeneter [Dutch];
GuÍpier de Perse [French]; Blauwangenspint [German]; Abelharuco-persa
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Coraciiformes
> Family: Meropidae
 |
 |
| Blue-cheeked bee-eater, Divundu,
Namibia. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Blue-cheeked bee-eater, Botswana. [photo
Neil Gray
©] |
The Blue-cheeked bee-eater is a palearctic breeding migrant,
arriving in southern Africa from October-November, and leaving for its Eurasian
breeding grounds in the period from March-May, mainly April. In southern Africa,
it generally prefers savanna, but it can also be found on open lake shores with
reeds, wooded swamps and bushy grassland. It is insectivorous, usually hawking
insects aerially, but also taking prey from the ground.
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across sub-Saharan Africa, largely excluding Sudan
and northern DRC. In southern Africa it is locally common in northern Namibia
(including the Caprivi Strip), northern and south-eastern Botswana, Zimbabwe,
Mozambique and north-eastern South Africa. It generally prefers savanna, open lake shores with reeds, wooded swamps
and bushy grassland.
|
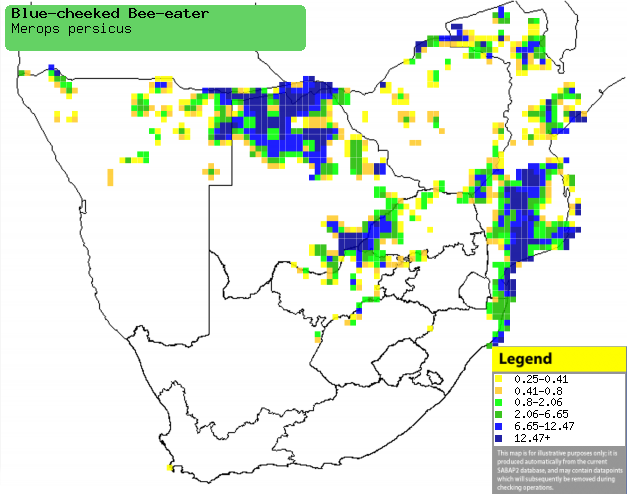 |
|
Distribution of Blue-cheeked bee-eater in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and Migrations
Palearctic breeding
migrant, arriving in southern Africa from October-November and leaving for its
Eurasian breeding grounds in the period from March-May.
Food
Insectivorous, usually
hawking insects aerially but also taking prey from the ground. Once it has
caught something it returns to its perch, where it kills and swallows its prey
(unless its a bee or wasp - in this case it has to first rub it against a branch
to disable its venom). The following prey items have been recorded in its diet:
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
