|
Sheppardia gunningi (East coast
akalat,
Gunnings robin)
Gunningse janfrederik [Afrikaans]; Blauwvleugel-akalat
[Dutch]; Rougegorge de Gunning [French]; Blauflügel-akalat [German];
Pisco-arisco [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Muscicapidae
For information about this species, see
birdinfo.co.za.
Distribution and habitat
It has localised populations from Kenya and Tanzania south
to Malawi and south-central Mozambique, which is within southern Africa's
border. Here it is locally fairly common in the undergrowth of evergreen forest,
especially with dense, moist thickets containing lianas, shrubs and saplings
beneath gap in the canopy left by a fallen tree.
|
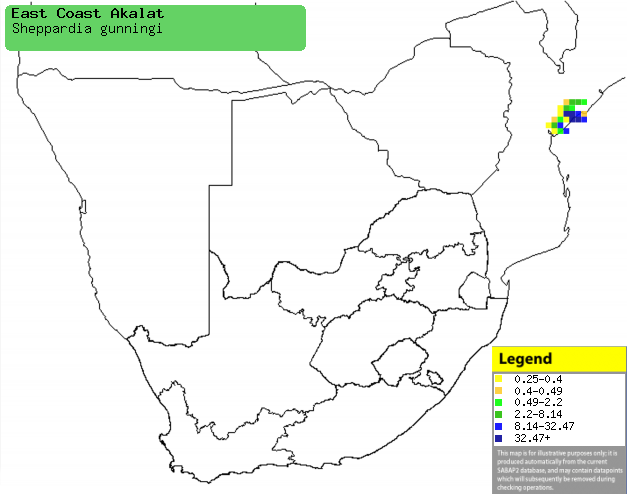 |
|
Distribution of East coast akalat in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats beetles, moths and ants, doing most of its
foraging from low perches, pouncing on prey on the ground. It may also follow
swarms of army ants, snatching they insects that flee from the leaf litter. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- The nest is a partially domed structure built of rootlets and typically
placed in leaf litter, between the roots of a broken stump.
- It has been recorded to lay 2-3 eggs in October, which are probably
incubated solely by the female.
- The chicks are intermittently brooded and fed by both parents.
Threats
Vulnerable, as due to its localised distribution it
is threatened by habitat disturbance and destruction, largely because of
deforestation.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
