|
Chlorocichla flaviventris
(Yellow-bellied greenbul, Yellow-bellied bulbul)
Geelborswillie [Afrikaans]; iBhada [Zulu];
Geelborst-buulbuul [Dutch]; Bulbul à poitrine jaune [French];
Gelbbrustbülbül [German]; Tuta-amarela [Portuguese]
Life > Eukaryotes > Opisthokonta > Metazoa (animals) > Bilateria > Deuterostomia > Chordata > Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class: Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial vertebrates) > Tetrapoda (four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota > Reptilia (reptiles) > Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria > Dinosauria (dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) > Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves (birds) > Order: Passeriformes > Family: Pycnonotidae
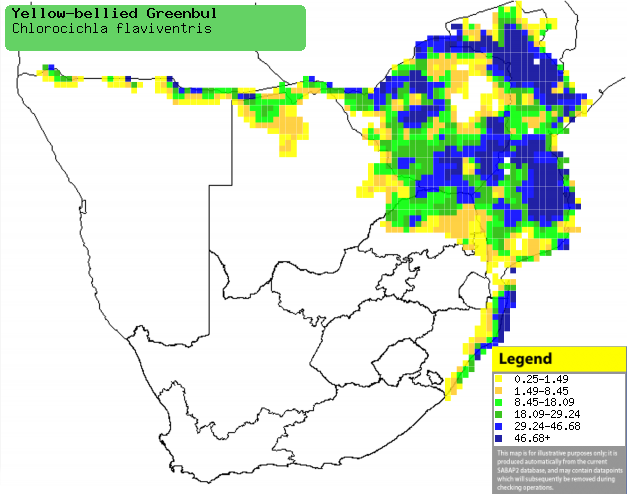
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Kenya and south-eastern DRC through Angola and
Zambia to southern Africa. Here it is common across Zimbabwe, Mozambique,
northern Namibia, eastern and northern Botswana, Limpopo Province and
KwaZulu-Natal. It generally prefers thick tangled undergrowth, especially in
clearings in riverine and coastal forest, miombo (Brachystegia) and
mopane (Colosphermum mopane) woodland, gardens, mangroves and semi-arid
bush.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Yellow-bellied greenbul in
southern Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from
first SA Bird Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of the
Falco biarmicus
(Lanner falcon)
Food
It mainly eats fruit, doing most of its foraging with other
bulbuls in the lower canopy, gleaning food from leaves and branches. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- fruit
- seeds
- flowers
- insects
- ticks taken from mammals such as:
- Aepyceros melampus (Impala)
- Sylvicapra grimmia (Common duiker)
- Tragelaphus angasii (Nyala)
- Oreotragus oreotragus (Klipspringer)
Breeding
- The nest is a fragile, thin-walled cup built of tendrils, twigs, dry grass
and other plant fibres; it is sometimes so flimsy that the eggs can be
visible from below! It is typically attached with spider web to the foliage
of a sapling, shrub or creeper.
- Egg-laying season is from September-March, peaking from
October-December.
- It lays 1-3 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about 14
days.
- The chicks are fed and brooded by both parents, leaving the nest after
about 16-18 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
