|
Cinnyricinclus leucogaster
(Violet-backed starling, Plum-coloured starling)
Witborsspreeu [Afrikaans]; Incuphabulongo [Swazi];
Xinwavulombe [Tsonga]; amethistspreeuw [Dutch]; Spréo améthyste [French];
Amethystglanzstar [German]; Estorinho-de-dorso-violeta [Portuguese] Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Sturnidae
 |
 |
| Violet-backed starling male. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
Violet-backed starling female, Kruger National
Park, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
 |
 |
| Violet-backed starling male, Erongo Mountains,
Namibia. [photo Johann Grobbelaar
©] |
Violet-backed starling female, Erongo Mountains,
Namibia. [photo Johann Grobbelaar
©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across much of sub-Saharan Africa, excluding Somalia
and central DRC, from Senegal to Ethiopia south to southern Africa. Here it is
seasonally common to abundant from northern Namibia and Botswana to Zimbabwe,
Mozambique and north-eastern South Africa, generally preferring riverine forest
and savanna woodland.
|
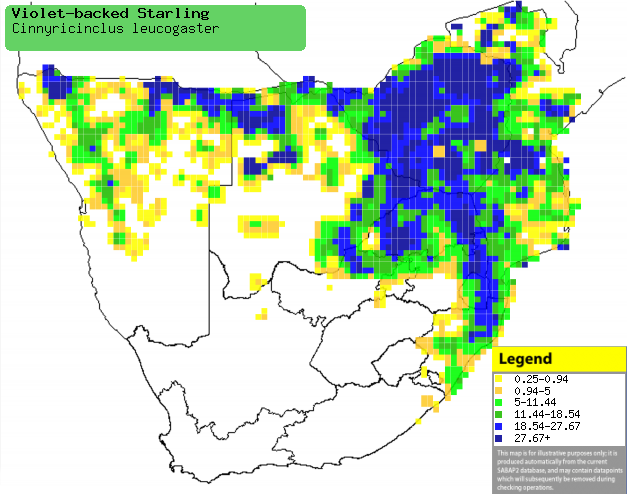 |
|
Distribution of Violet-backed starling in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of
Falco peregrinus
(Peregrine falcon).
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Lesser honeyguide.
Movements and migrations
Intra-African migrant, living in tropical
Africa before heading south to southern Africa to breed, mainly
arriving in September. It often moves locally in response to tree's
fruiting cycles, eventually leaving around May.
Food
It eats insects and fruit, gleaning food from leaves and
branches and occasionally hawking prey aerially. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Insects
- Fruit
- Celtis (stinkwood)
- Rotheca myricoides (Cats-whiskers)
- Boscia albitrunca (Shepherds-tree)
- mistletoes
- Tapinanthus oleifolius
- Tapinanthus leendertziae
- Morus alba (Mulberry)
Breeding
- The nest is a structure built of coarse plant material and leaves,
typically placed in a tree cavity or hollow fence post.
- Egg-laying season is from October-March.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
12-14 days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents on a diet of mainly insects, leaving
the nest after about 17-21 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
