|
Amadina fasciata (Cut-throat
finch)
Bandkeelvink [Afrikaans]; Enzunge (applied to some of the
bishops, widows and sparrows) [Kwangali]; bandvink [Dutch]; Amadine
cou-coupé [French]; Bandfink [German]; Degolado [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Estrildidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across the Sahel from Senegal to Ethiopia south to
Kenya and Tanzania, with a separate population in the area from southern Angola,
Zambia and Malawi to southern Africa. Here it is uncommon to fairly common from
localised parts of Mozambique through Zimbabwe to Botswana and north-eastern
South Africa, while scarce in Namibia, generally preferring savanna woodland.
|
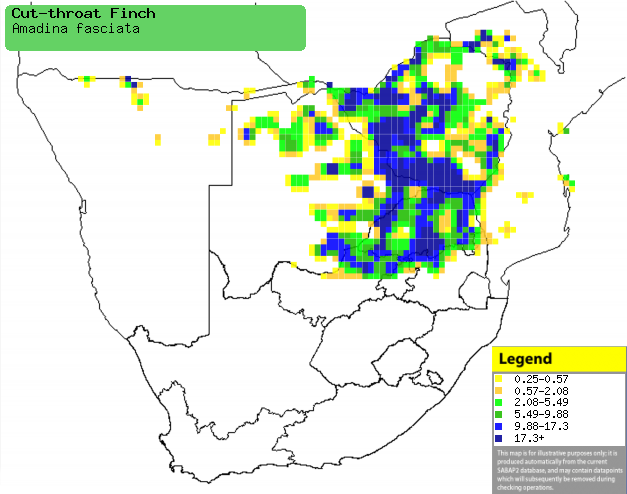 |
|
Distribution of Cut-throat finch in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of
Falco peregrinus
(Peregrine falcon).
Movements and migrations
Generally resident while breeding, but in the
non-breeding season it is nomadic.
Food
It does most of its foraging on the ground, mainly feeding
on seeds and termites.
Breeding
- The nest is built by both sexes, consisting of a ball of grass with a
short entrance tunnel, while the interior is lined with feathers. It is
typically placed in the old nest of a
Ploceus weaver,
Red-billed buffalo weaver,
Red-headed weaver or
woodpecker, rarely using a hole in a
fence post instead.
- Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking from December-April.
- It lays 2-7, usually 4-6 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for
about 12-13 days.
- Not much is known about the chicks, other then that they leave the nest
after about 21-23 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
