|
Crithagra scotops (Forest canary)
[= Serinus scotops]
Gestreepte kanarie [Afrikaans]; Unotswitswitswi [Xhosa];
boskanarie [Dutch]; Serin forestier [French]; Schwarzkinngirlitz [German];
Canário-da-floresta [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Fringillidae
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to South Africa marginally extending into Lesotho
and Swaziland, occurring from Limpopo Province south to KwaZulu-Natal and down
the southern coast to the Eastern and Western Cape. It generally prefers patches
of indigenous forest and coastal thicket in valley bushveld, sometimes moving
into adujacent dense vegetation to forage, such as tall Protea woodland,
patches of tall shrubs such as Gonna (Passerina vulgaris), orchards,
well-wooded gardens and alien tree plantations.
|
 |
|
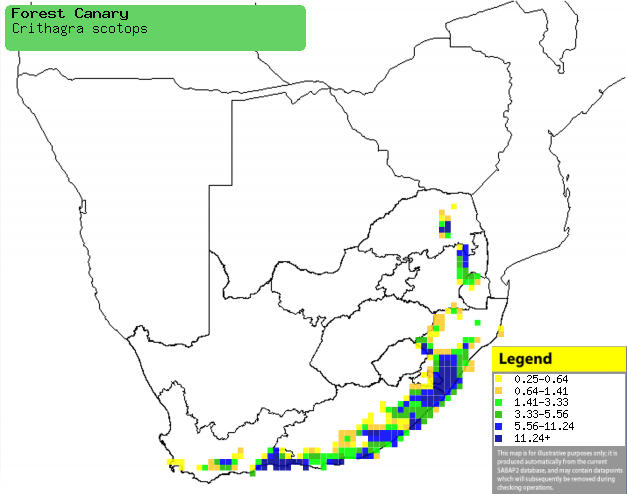
Distribution of Forest canary in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of
Falco peregrinus
(Peregrine falcon).
Movements and migrations
Resident and sedentary, although it may make
local movements in Winter in search of new food sources.
Food
It mainly eats seeds, fruit, flowers and leaves, doing most
of its foraging on the ground or in vegetation, plucking food directly from
plants. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Plants
- seeds
- Panicum (Guinea grasses)
- oats
- Alyssum
- Passerina corymbosa (gonna)
- fruit
- Anthospermum (jackalsstert)
- Plectranthus
- Ficus (figs)
- flowers of Penaea cneorum (Penaeaceae)
- leaves
- Senecio (creeping groundsel)
- Ptaeroxylon obliquum (Sneezewood)
Breeding
- Monogamous territorial usually solitary nester, although two nests were
once recorded to be only two metres apart.
- The nest is built by the female, consisting of a bulk cup of moss and
fine stems, lined with fibrous lichen and typically placed in the fork of a
tall shrub or small tree on the forest edge.
- Egg-laying season is from October-March.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about 14
days.
- The chicks are fed by the female with food provided by the male, leaving
the nest after about 15-19 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
