|
Delichon urbicum (Common
house-martin, House martin)
[= Delichon urbica]
Huisswael [Afrikaans]; Sisampamema (generic term for swallows,
martins, swifts and spinetails) [Kwangali]; Lekabelane (generic term for
swallows or martins) [South Sotho]; huiszwaluw [Dutch]; Hirondelle de fenÍtre
[French]; Mehlschwalbe [German]; Andorinha-dos-beirais [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Hirundinidae
Distribution and habitat
Its breeding territory stretches from Britain and
north-west Africa to central Asia. In the non-breeding season it migrates to
Africa from southern Mauritania to Uganda and Ethiopia south to southern Africa.
Here it occurs in patches across Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Botswana, Namibia,
Lesotho, Swaziland and South Africa, from the Kruger National Park and Gauteng
through to KwaZulu-Natal, the Eastern and Western Cape. It occupies a variety of
open habitats, including fynbos, savanna, grassland and agricultural areas, but
it is most common in mountainous or hilly areas, such as the Drakensberg and
eastern highlands of Zimbabwe.
|
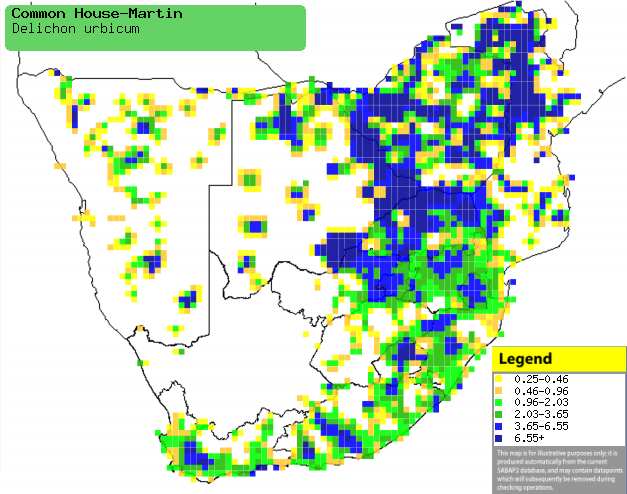 |
|
Distribution of Common house martin in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It exclusively eats arthropods, doing most of its foraging
at high altitudes along with other swallows and swifts. It may also descend to
near ground level to feed on insects scared of by bush fires or tractors.
Breeding
- There are have been sightings of pairs building nests in South Africa and
Namibia, all dating from the pre 1970s. Most lack any details accept for two
sightings in the late 60s - with both there was no evidence that suggest the
breeding attempt went beyond the nest-building stage.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
