|
Podiceps cristatus (Great
crested grebe)
Kuifkopdobbertjie [Afrikaans]; Nyakupetana, Ripetani
[Tsonga]; Fuut [Dutch]; Grèbe huppé [French]; Haubentaucher [German];
Mergulhão-de-crista [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves (birds) > Order:
Ciconiiformes
> Family: Podicipedidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across much of the Old World, in Australia, Eurasia
and sub-Saharan Africa: from Ethiopia to Tanzania and eastern DRC. It has an
isolated population in southern Africa, centred around the Western Cape and
Gauteng (extending into south-eastern Botswana), while more
scarce elsewhere in southern Africa. It generally favours large inland lakes,
dams and pans, especially if fringed with vegetation; it occasionally moves to saltpans.
|
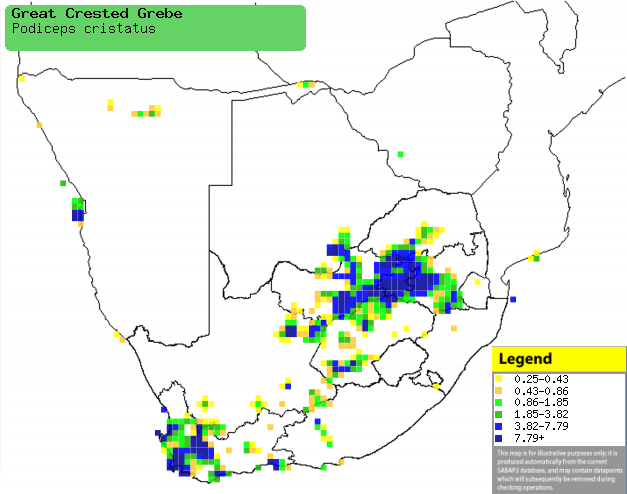 |
|
Distribution of Great crested grebe in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Generally resident and nomadic, sometimes
travelling long distances to reach seasonally flooded areas.
Food
It almost exclusively eats small fish, caught by diving in
stints of about 20-25 seconds. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Vertebrates
- Invertebrates
- crustaceans
- aquatic insects
Breeding
- Monogamous, territorial solitary or gregarious nester, as multiple pairs
may breed a few metres apart. Like many grebes it performs an elaborate
courtship display.
- The nest (see images below) is built by both sexes in roughly eight days
of the courtship period, consisting of a platform of reeds (Phragmites),
bulrushes (Typha) and other material, such as khaki weed (Tagetes)
and grass, although it may be made entirely of soft plants including
pondweed (Potamogeton). It is typically attached to water plants or
submerged woody shrubs in open water, and has to be constantly maintained
to prevent it from sinking into the water.
 |
 |
| Great-crested grebe nest with eggs,
Naboomspruit, South Africa. [photo
Warwick Tarboton ©] |
Great crested grebe on nest. [photo Peter Steyn
©] |
- Egg-laying season is year-round in Botswana, from October-December in the
Western Cape and mainly from March-July elsewhere in South Africa.
- It lays 2-7 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 27-30
days.
- The chicks slip into the water almost immediately after
hatching, and are regularly carried on the back of either adult for up to
two weeks; the adult not on carrying duty fishes and gives the food to the
other parent and chicks. Once they reach about 28-42
days old, the brood are divided into two groups, each cared for by a parent.
They can forage for themselves at approximately 56 days old and can fly at
about 70-79 days old, becoming fully independent a few weeks later.
Threats
Not threatened, although it often leaves bodies of water which are
used regularly by humans for recreation.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
