|
Porzana porzana (Spotted crake)
Gevlekte
riethaan [Afrikaans]; Katukutuku (generic term for crake) [Kwangali];
Porseleinhoen [Dutch]; Marouette ponctuée [French]; Tüpfelsumpfhuhn
[German]; Franga-d'água-grande [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Gruiformes >
Family: Rallidae
Distribution and habitat
Breeds from north-western China to western and southern
Europe, heading south in the non-breeding season to the Mediterranean region and
Africa, from Egypt south through eastern Sudan, Ethiopia, Tanzania and
eastern DRC to Zambia, Angola and southern Africa. Here it is generally uncommon
in isolated patches of north-eastern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip),
Botswana and Zimbabwe, while scarce in the Limpopo Province.
|
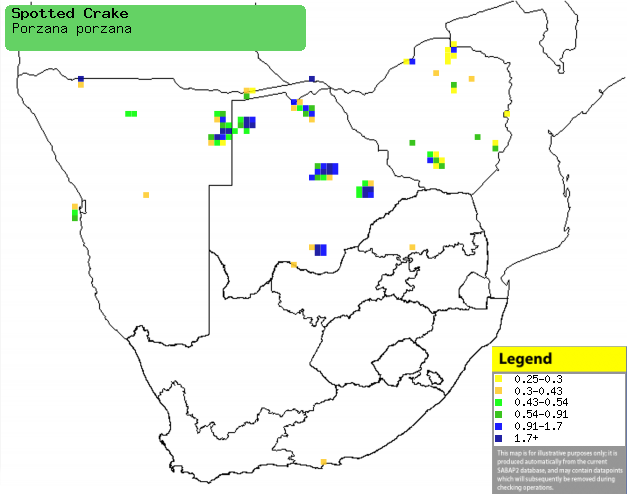 |
|
Distribution of Spotted crake in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Movements and migrations
Palearctic breeding migrant, arriving in mid
December, with numbers peaking from January-March before most of
them leave in March and April. It mainly migrates at night, flying
just 1-3 metres above ground.
Food
Mainly eats earthworms, spiders, fish and seeds, doing most
of its foraging by walking along muddy shores or on lily pads, probing the
ground and vegetation in search of food.
Threats
Not threatened globally, although its population and range
have been on the decrease.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
