|
Vidua funerea (Dusky indigobird, Variable indigobird,
Black widowfinch)
Gewone blouvinkie [Afrikaans]; Groene atlasvink [Dutch];
Combassou noir [French]; Purpur-atlaswitwe [German]; Viúva-negra [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Viduidae
 |
 |
|
Dusky indigobird male, Pietermaritzburg,
KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. [photo
Alan Manson
©] |
Dusky indigobird female, Pietermaritzburg,
KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. [photo Alan Manson
©] |
For information about this species, see
www.birdforum.net/opus/Variable_Indigobird
Distribution and habitat
Although it has an isolated population in Nigeria and
Cameroon, the bulk of its population occurs in patches from Kenya through
Tanzania, Malawi and Zambia to southern Africa. Here it is locally common in
Zimbabwe's eastern highlands and adjacent Mozambique, extending south to eastern
South Africa, from Limpopo Province to the Eastern Cape. It generally prefers
mesic woodland, edges of montane and riverine forests, grassy vegetation with
weeds, orchards with annual grasses, lightly cultivated land and village
gardens.
|
 |
|
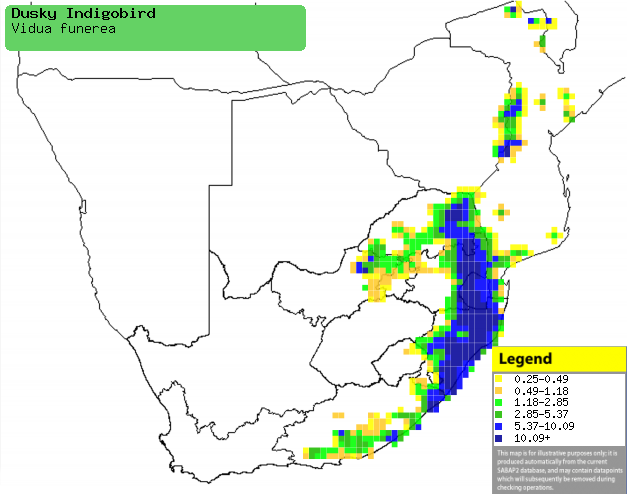
Distribution of Dusky indigobird in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of the Domestic cat (Felis
cattus).
Food
It mainly eats grass seeds uncovered in the soil,
supplemented with termite alates caught aerially.
Breeding
- It is a polygynous brood parasite, with males defending a territory
surrounding a prominent perch which it uses to display on. The only bird
recorded as its host is the
African firefinch.
- The female eats any existing eggs in the firefinch nest before laying a
single one of its own, laying eggs in sets of three.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
