|
Vidua purpurascens (Purple
indigobird, Purple widowfinch)
Witpootblouvinkie [Afrikaans]; Purperstaalvink [Dutch];
Combassou violacé [French]; Weißfuß-atlaswitwe [German]; Viúva-púrpura
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Viduidae
 |
 |
|
Purple indigobird male, Nylsvlei, South Africa. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Purple indigobird female, Thornybush Game Reserve,
South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
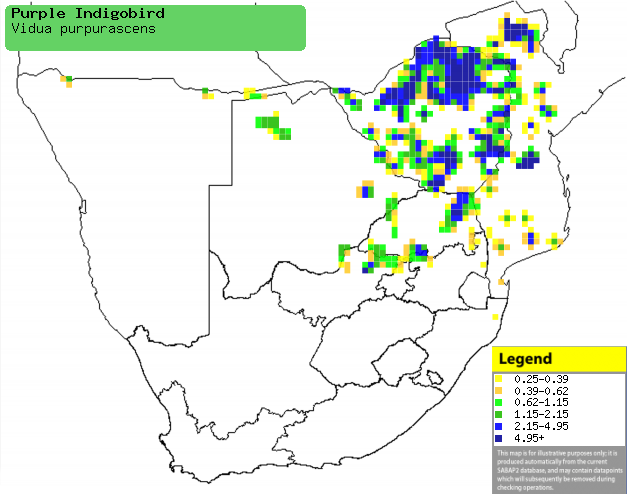
Distribution and habitat
Although it occupies isolated patches of Tanzania and
Zambia, the bulk of its population occurs from Angola to Zambia, Malawi and
southern Africa. Here it is uncommon to locally common in Zimbabwe, Mozambique
and north-eastern South Africa, while more scarce in Botswana and Namibia. It
generally prefers dry woodland, riverine forest, rank grass and edges of
thickets and cultivated fields.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Purple indigobird in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats grass seeds, doing most of its foraging on
bare ground, scratching the soil with its feet to uncover seeds. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet in Zambia:
- Grass seeds
- Echinochloa colonum (Swamp grass)
- Setaria
- Urochloris
- Dactycynodon
-
Termite alates
Breeding
- Polygynous brood parasite, with each male defending a territory centered
on a prominent perch, which is used for calling and displaying. Intruders,
which can be the same species or a different indigobird, are aggressively
chased out of the territory by the male. Its sole host is the
Jameson's firefinch,
it has not been recorded to parasitise or mimic any other species.
- Egg-laying season is from January-May.
- It lays one egg per day in sets of 3-4, taking a few days break in
between sets.
- It is thought that the chick is reared alongside Jameson's firefinch
young, as fledglings of the two species have been recorded together in
family groups.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
