|
Panthera leo (Lion)
leeu [Afrikaans]; Löwe [German]; lion d' Afrique [French]; simba [Swahili];
isilwane, indau, ingonyama,ibhubezi [isiN debele]; ingonyama, ibhubesi [isiXhosa];
ingonyama, ibhubesi, imbube [isiZulu]; tau [Sepedi] [Sesotho] [Setswana] [Lozi]; shumba [Shona]; libhubesi, ingwenyama [siSwati]; nghala, n'shumba [Xitsonga];
ndau [Tshivenda]; andavu [Yei]; Xamm [Nama] [Damara]
Life
>
Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta >
Metazoa (animals) > Bilateria > Deuterostomia >
Chordata > Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) >
Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost
fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish) > Stegocephalia
(terrestrial vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Synapsida (mammal-like reptiles) > Therapsida > Theriodontia
> Cynodontia > Mammalia (mammals)
> Placentalia (placental mammals) > Laurasiatheria
> Ferungulata > Ferae > Carnivora > Family:
Felidae (cats) > Subfamily: Pantherinae
One of Africa’s “Big Five”. The largest of the African cats and the most
social member of the cat family living in prides of 3-30
individuals. Lionesses give birth to their cubs under cover
away from the pride and will only return to the pride when the cubs
are 6-8 weeks old. Male lions will often kill any existing cubs in
the pride after they successfully depose the dominant male or male
group. This results in the females being able to produce this new
male's cubs sooner. Prey varies greatly - from mice through to young
elephants.
Identification
Male and females are easy to tell apart as sexual
dimorphism is marked. The males are identified by a mane of long
hair, females are also much smaller. The mane varies from
tawny-brown to black in colour, and extends from the sides of the
face to the neck, shoulders and chest.
Size
Male: Body Length 2.5 -3.3 m; height at
shoulder 1.2 m; weight range 150 - 225 kg.
Female: Body Length 2.3 – 2.7 m; height at shoulder 1.0 m; weight
range 110 – 152 kg.
Dental Formula
I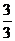 C C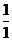 P P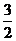 M M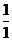 =
30 =
30
Distribution and habitat
Occur mainly in Africa south of the Sahara but
was once more widespread than this, including around the
Mediterranean, the Middle East and parts of Asia. Amazingly, there
is still a last surviving population of the Asiatic lion in
Northwest India where it is found in and around the Gir Forest. Up
until about 10 000 years ago, lions were even found in the Americas.
In the southern
African subregion lions are restricted to northern and eastern
regions. They tolerate a wide range of habitats from desert
fringe to woodland or open savanna. They once occured in the Cape
and these lions had darker mains and previously were
distinguished as a separate subspecies although genetic evidence
suggests that such subspecies status is not justified.
General behaviour
The most social member of the cat family living
in prides of 3-30 individuals. Pride sizes vary depending on the environmental
conditions. A pride consists of 1 or more dominant males, a dominant
lioness and other sub ordinate females, with associated sub-adults
and cubs. More than one male can be associated with a pride but they
form a coalition and are usually siblings. They mark their territory
and challenge any intruders. Male lions will often kill any existing
cubs in the pride after they successfully depose the dominant male
or male group. This results in the females being able to produce
their cubs sooner. Young males are driven from the pride and exist
as bachelor groups until they can successfully challenge for a pride
of their own.
Lions are active during the cooler parts of the
day and during the night. The roaring of lions during the night is
one of the characteristics of the African bush. These roars can be
heard for several kilometers and are a signal that the territory is
occupied.
Hunting and food
Although known as an active hunter, lions are
great opportunists and will take advantage of any food in the
immediate vicinity. They will chase other predators off their kills,
this includes cheetah, leopard and hyena, and they also scavenge.
The females undertake most of the hunting, although the pride male
will always feed first.
Prey can include mice to young elephants as well as a
wide variety of none mammalian prey.
 |
|
Female lion at Buffalo kill, Kruger National Park,
South Africa. [photo Arno Meintjes
©] |
Reproduction
The gestation period lasts about 110 days. Lionesses give birth to their cubs under cover
away from the pride and will only return to the pride when the cubs
are 6-8 weeks old. As a lioness will allow any pride cub to suckle
they will delay bringing young cubs to the pride if cubs older than
3 months are present. Older cubs will not allow the young cubs to
suckle. Cubs remain with their mother for approximately 2 years.
Life span
Up to 60 years has been recorded.
Conservation
Lions are now largely restricted to the major
conservation areas, and are still hunted outside these protected
reserves. While they rarely attack humans unless provoked, they are
still considered a dangerous animal and for this reason their
presence is not tolerated. They conflict with stock farmers in
certain areas. .Their conservation status is listed as vulnerable
and they are CITES listed.
Links
Text by Denise Hamerton |
