|
Panthera pardus (Leopard)
luiperd [Afrikaans]; Leopard [German]; panthère,
léopard [French]; chui [Swahili]; ingwe [isiNdebele]
[isiXhosa] [isiZulu] [siSwati] [Xitsonga]
[Tshivenda]; nkwe [Sesotho]; nkwe [Setswana];
mdaba, isngwe [Shona]; ngwe [Lozi]; ungwe [Yei]; |Garub
[Nama] [Damara]; ngwi [Herero] [Ovambo]
Life
>
Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta >
Metazoa (animals) > Bilateria > Deuterostomia >
Chordata > Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) >
Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost
fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish) > Stegocephalia
(terrestrial vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Synapsida (mammal-like reptiles) > Therapsida > Theriodontia
> Cynodontia > Mammalia (mammals)
> Placentalia (placental mammals) > Laurasiatheria
> Ferungulata > Ferae > Carnivora > Family:
Felidae (cats) > Subfamily: Pantherinae
 |
|
Leopard, Kruger National Park, South Africa. [photo Arno Meintjes
©] |
 |
 |
|
Leopard, Sabi Sands, Kruger National Park, South
Africa. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
Leopard, Kruger National Park, South Africa. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
One of the “Big Five” in Africa, leopards are a
highly popular tourist attraction in national parks and reserves,
which makes them
highly prized and an important source of income. Males are solitary
and females rear the cubs. Prey is varied, ranging from
invertebrates through to medium-sized antelope. Leopards are found
in the mountains of the Western Cape but are rarely seen.
Description
The characteristic dark rosette shaped spots on the
coat of the back, flanks and upper limbs provide it with excellent
camouflage. Males are about 50% larger than females. In South Africa
leopards from the mountain ranges of the Cape Province are much
smaller than those from the northern part of the country.
Size
Total Body length 160-210 cm, body mass 20 –90
kg (males) and 17 – 60kg (females).
Dental Formula
I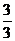 C C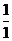 P P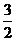 M M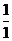 =
30 =
30
Distribution and habitat
The leopard is the most widespread member of
the cat family with a distribution throughout sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle-East,
extending through Asia to China. Widely distributed in southern Africa, although
south of the Orange River it only remains in the more mountainous
and rugged areas. It is found in a wide range of habitats where there
is reasonable cover, from mountainous regions to coastal plains, in
both high and low rainfall areas.
General behaviour
Leopards are good climbers, this enables them
to escape harassment and competition from other predators such as
lions and hyena. Kills are usually hidden in thick vegetation but if
there is intense competition from other predators leopards will drag
their prey up a tree and store it in the branches.
Male leopards are solitary, while females spend a large part of
their lives with their cubs. The home ranges of leopards are
extremely variable in size, but generally the availability of
suitable prey will affect the territory size. The more food that is
available, the smaller the range will be, and the denser the
distribution of the animals. Leopards make a rough rasping sound,
similar to a rough saw cutting through wood.
Hunting and food
They stalk their prey, relying on
concealment before making a short fast dash or pouncing to capture
it. They often kill with a bite to the back of the neck.
Food is varied and includes insects,
rodents, birds, reptiles and medium sized antelope. Also eats carrion.
 |
|
Leopard feeding on its kill, Kruger National Park,
South Africa. [photo
Bernard Dupont ©] |
 |
 |
|
Female cub dining on impala in Sabi Sands, Kruger
National Park, South Africa. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
Leopard feeding on slain
Vervet Monkey,
Kruger National Park, South Africa. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
Reproduction
Gestation period is about 100 days. The female raises her litters of 2-3 cubs
alone. The cubs are usually hidden in a cave or rock crevice for the
first 6 weeks after birth. They will remain with their mother until
they are 18-20 months old, when she will encourage them to leave and
will then mate again.
Life span
14 years (up to 20 in captivity)
Conservation
Numbers are declining in some areas as a result
of habitat loss and leopards are trapped and killed in areas where
they clash with stock farmers. Leopards are protected in South
Africa and a permit has to be obtained from a conservation agency
before a farmer has permission to trap or hunt a “problem” leopard.
Usually conservation agencies will try to remove a leopard from
areas where it is in conflict with farmers and relocate it. When
trapped, wounded or threatened the leopard can be extremely
dangerous.
Links
Text by Denise Hamerton |
