|
Parahyaena brunnea
(Brown hyaena)
strandjut, bruinhiŽna, strandwolf [Afrikaans];
Braune Hyšne, Schabrackenhyšne [German];
hyŤne brune [French];
impisi, ipisi enzotho [isiNdebele];
ingqawane, inchuka [isiXhosa];
isidawana [isiZulu];
sephiribjŰkwane, phiribjŰkwane [Sepedi];
phiribjokwane, phiri, thamahane [Sesotho];
phiri, phiritshwana, lefiritshwana, phiri Íntsho, phiri Íntshonyana, mosonokwane,
mosonolokwane, setinikwana, sethenekwane [Setswana];
bere [Shona];
imphisi [siSwati];
mhisi, mhisana [Xitsonga];
tshivhingwi [Tshivenda];
Hiras [Nama] [Damara];
nutsa [San]
Life
>
Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta >
Metazoa (animals) > Bilateria > Deuterostomia >
Chordata > Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) >
Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost
fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish) > Stegocephalia
(terrestrial vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Synapsida (mammal-like reptiles) > Therapsida > Theriodontia
> Cynodontia > Mammalia (mammals)
> Placentalia (placental mammals) > Laurasiatheria
> Ferungulata > Ferae > Carnivora > Family: Hyaenidae (hyenas)
> Subfamily: Hyaeninae
 |
|
Parahyaena brunnea
(Brown hyaena), Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, South Africa. [photo
Bernard Dupont ©] |
 |
 |
|
Brown hyaena. [photo
Callie de Wet ©] |
Parahyaena brunnea
(Brown hyaena), Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, South Africa. [photo
Bernard Dupont ©] |
Identification
Brown hyaena have a typical “up-hill” shape,
with heavily build forequarters that stand significantly higher than
the lighter hindquarters. The head is large with longish pointed
ears and a black muzzle. It has a coat of long dark brown hair and
mantle of lighter coloured hair on the back and shoulders. The legs
are striped black and light brown. The tail is short and bushy. The
powerful jaw structure and large teeth ensure that the whole prey
animal is eaten including crushing the large bones to extract the
marrow. Hyena droppings are characteristically white because of the
very high bone content.
Size
Total Body Length: 130-160 cm; height at
shoulder 80 cm; weight range 47 kg (male) and 42 kg (female)
Dental Formula
I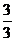 C C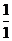 P P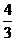 M M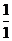 =
34 =
34
Distribution and habitat
Used to occur widely in southern Africa in arid
and semi-arid habitats,
but now limited to the Kalahari and arid Namibian coastal belt, only
rarely seen south of the Orange River.
General behaviour
Brown hyaena are nocturnal and usually seen
alone, although several animals may share a territory. The animals
that share a territory are usually an extended family unit and will
all assist with raising cubs. Territories are marked using droppings
and anal gland secretions. Nomadic males range through several
territories and mate with receptive females. It is interesting that
males within each group do not generally mate with the females in
the same group. Unlike the Spotted hyaena this species not
particularly vocal.
Food
Predominantly a scavenger, but includes a
wide range of small vertebrates, insects and fruits.
Reproduction
A litter of 1-4 cubs is born in a underground
burrow after a gestation period of 90 days.
Life span
14 years
Conservation
The brown hyaena used to occur widely in
southern Africa but the numbers are drastically reduced today. This
species has been relentlessly hunted by stock farmers that regard it
as a threat to their sheep and goat stocks. Loss of habitat as a
result of farming has also contributed.
Text by Denise Hamerton |
