|
Aquila nipalensis (Steppe
eagle)
Steppe-arend [Afrikaans]; Ukhozi (generic term for eagle)
[Xhosa]; Steppearend [Dutch]; Aigle des steppes [French]; Steppenadler
[German]; Įguia-das-estepes [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Falconiformes
> Family: Accipitridae
> Genus: Aquila
Distribution and habitat
Breeds from southern Ukraine to central Asia, heading south
in the non-breeding season to India and Africa.
In southern Africa it is locally common in patches of northern Namibia (including the Caprivi
Strip), northern and eastern Botswana, Zimbabwe, western Mozambique and
north-eastern South Africa. It generally prefers savanna, open woodland and
grassland; it is largely absent from mountainous and densely forested areas.
|
 |
|
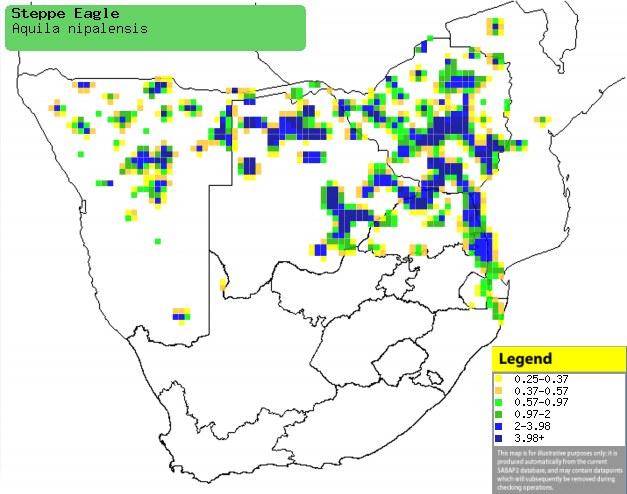
Distribution of Steppe eagle in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Palearctic breeding migrant, arriving in
southern Africa in the period from October-November. It then moves
nomadically in search of termite alate emergences, eventually departing
in the period from March-April.
Food
It feeds mainly on termite alates, gathering in flocks of
up to about 800 individuals at termite alate emergences, chasing them both in
the air and on the ground. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- termite alates
- Hodotermes mossambicus (Northern harvester termite)
- recently fledged Red-billed queleas (Quelea quelea)
- carrion
Threats
Numbers of migrants in Israel have halved since 1975, which
is thought to have been largely caused by radioactive fallout from Chernobyl; it
is also frequently electrocuted on power lines.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
