|
Aviceda cuculoides (African
cuckoo hawk, Cuckoo hawk)
Koekoekvalk [Afrikaans]; Afrikaanse koekoekswouw [Dutch];
Baza coucou [French]; Kuckucksweih [German]; Falc„o-cuco [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Falconiformes
> Family: Accipitridae
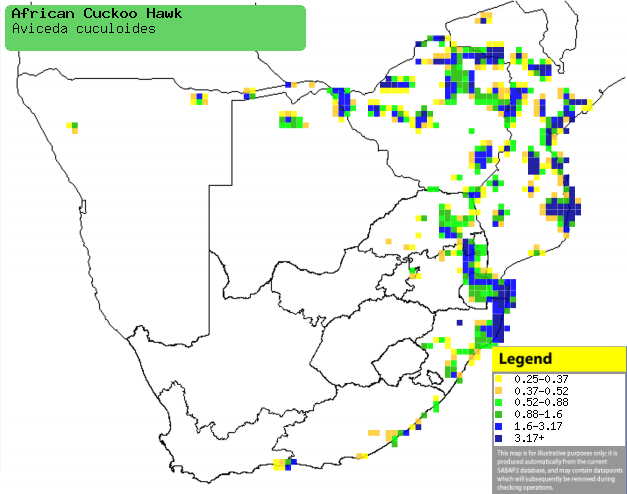
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across much of sub-Saharan Africa; in southern
Africa it
is generally scarce in Mozambique, Zimbabwe, northern Botswana, Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip) and eastern South Africa, with an isolated
population in the east of the Western Cape. It generally prefers woodland, the
understorey and edges of forest and plantations of alien trees.
|
 |
|
Distribution of African cuckoo hawk in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Movements and migrations
It is largely resident, although it may make
local movements in Winter.
Predators and parasites
The chicks have been recorded as prey of
Aquila wahlbergi (Wahlberg's
eagle).
Food
It mainly eats reptiles and insects, hunting by flying from
tree to tree, searching for from its perch before flying to pluck the prey item
from the canopy or ground. The following food items have been recorded in its
diet:
- Animals
- reptiles
- frogs
- fish
- mammals
- birds
- invertebrates
Breeding
- Monogamous, solitary nester, performing spectacular aerial displays in the
run-up to the breeding season.
- The nest (see image below) is built by both sexes in about 11 days,
consisting of an untidy platform of twigs, vines and leaves and lined with
leaves, grass and small bits of sticks. It is typically placed in the
highest branches of a tree, roughly 10-30 metres above ground.
 |
|
|
African cuckoo hawk nest with eggs, Nylsvley area,
South Africa. [photo
Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- It lays 1-2, rarely 3 eggs in the period from September-March; egg-laying
season peaks
from October-December.
- The chicks are fed and brooded by both parents, leaving the nest after
about 28 days and taking their first flight a few days later, remaining
dependent on their parents for another week or so.
Threats
Previously suspected to be threatened in the early 1980's,
but it is now thought to be not threatened in southern Africa.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts - Birds of
southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker Bird Book
Fund, Cape Town.
|
