|
Apus apus (Common swift, European
swift)
Europese windswael [Afrikaans]; Ihlabankomo, Ihlankomo
(generic names for swifts) [Xhosa]; iJankomo, uHlolamvula [Zulu]; Lehaqasi
(generic term for swifts) [South Sotho]; Nkonjana (generic term for swift)
[Tsonga]; Pêolwane, Phêtla (generic terms for swifts, martins and swallows)
[Tswana]; Gierzwaluw [Dutch]; Martinet noir [French]; Mauersegler [German];
Andorinhão-preto-europeu [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves (birds) > Order: Apodiformes >
Family: Apodidae
|
 |
 |
|
Common swift. [photo
© H. Robertson, Iziko] |
Common swift, West Coast National Park, South
Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
The Common swift breeds from China through Asia to Europe and
and North Africa, with non-breeding grounds encompassing the whole of
sub-Saharan Africa. It is a palearctic non-breeding migrant, usually arriving in
southern Africa in October-November, leaving roughly from January-March. It
exclusively eats arthropods, foraging at much higher altitudes than
local-breeding swifts, often reaching heights of 1500-3000 m above ground,
usually flying at 36-90 km/hr, but it has been known to reach 216 km/hr in
certain conditions! Interestingly, it is permanently airborne in non-breeding
grounds, roosting on the wing.
Distribution and habitat
Breeds from China through Asia to Europe
and North Africa, with non-breeding grounds encompassing the whole of
sub-Saharan Africa. It occurs in patches across southern Africa in a wide range of habitats, although it generally prefers open, semi-arid
areas.
|
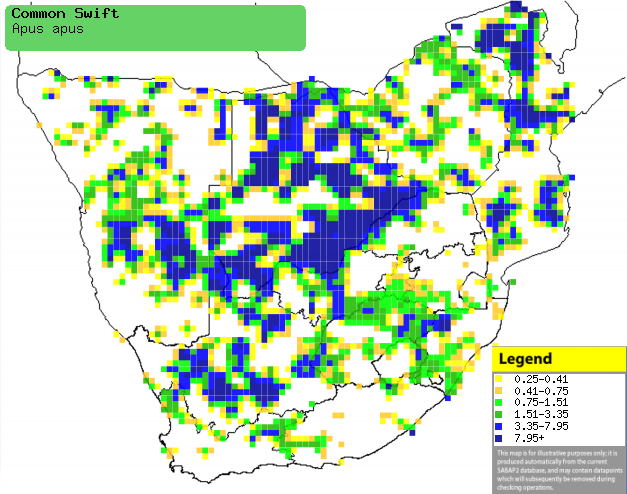 |
|
Distribution of Common swift in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Palearctic non-breeding migrant,
arriving in southern Africa in the period from October-November, leaving from
January-March.
Food
It feeds exclusively on arthropods, especially insects 2-12 mm long,
foraging at much higher altitudes than
local-breeding swifts, often reaching heights of 1500-3000 m above ground. It
usually flies at 36-90 km/hr, but it has been known to reach 216 km/hr in
certain conditions! If it is cold and wet it descends lower, often feeding on
termite alate emergences. Interestingly, it is permanently airborne in
its non-breeding grounds, roosting on the wing.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact has a stable estimated population
of 25 million individuals.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
