|
Campephaga flava (Black
cuckooshrike)
Swartkatakoeroe [Afrikaans]; Umthethi (also applied to
Olive bush-shrike - CHECK), Usinga Olumnyama [Xhosa]; iNhlangu [Zulu]; Rankwitidi
[North Sotho]; Kaapse rupsvogel [Dutch]; Échenilleur à épaulettes jaunes
[French]; Kuckuckswürger [German]; Lagarteiro-preto [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Campephagidae
 |
|
Black cuckooshrike female, Helderberg Nature
Reserve, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
 |
 |
|
Black cuckooshrike female. [photo Martin Goodey
©] |
Black cuckooshrike male, Weenen Game Reserve,
KwaZulu-Natal Midlands, South Africa. [photo Alan Manson
©] |
For information about this species, see
www.birdforum.net/opus/Black_Cuckooshrike Distribution and habitat
Mainly occurs in Africa south of the equator from southern
Sudan, Kenya and the DRC down to southern Africa. Here it is generally uncommon,
occupying much of Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Swaziland, northern and south-eastern
Botswana and northern Namibia. In South Africa it can be found across the Kruger
National Park and eastern KwaZulu-Natal, extending down the coast to the
south-western cape. It generally favours Broad-leaved burkea and mixed woodland,
also occurring along the edges of evergreen forest and in well-wooded gardens.
|
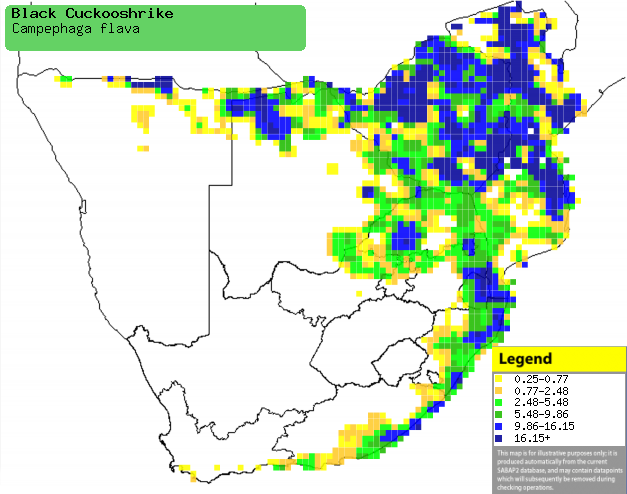 |
|
Distribution of Black cuckooshrike in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats insects, getting most of its prey by
gleaning leaves and branches, often joining mixed species foraging flocks. The
following food items have been recorded in its diet:
Breeding
- The nest is built solely by the female and consists of a cup built of of
moss, lichens and old-man's beard lichen (Usnea) bound together with spider
web. It is usually placed in a vertical fork of a tree branch, often high up
in the tree.
 |
|
|
Black cuckooshrike nest with eggs, Sericea, South
Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- It lays 1-3 eggs, which are incubated by the female for about 20 days -
the male feeding her at the nest.
- The checks are fed by both adults but brooded only by the female,
leaving the nest after about 20-23 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
