|
Centropus cupreicaudus
(Coppery-tailed coucal)
Grootvleiloerie [Afrikaans]; Mukuku (generic term for
cuckoos and coucals) [Kwangali]; Koperstaartspoorkoekoek [Dutch]; Coucal des
papyrus [French]; Angola-mönchskuckuck [German]; Cucal-cauda-de-cobre
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Cuculiformes
> Family: Centropidae
The Coppery-tailed coucal is endemic to south-central Africa,
occurring in a small band from south-western Angola to the Caprivi Strip and
northern Botswana, preferring dense waterside vegetation. It eats a wide range
of animals, including grasshoppers, frogs and fish. The nest is a hastily built
ball of grass, placed in dense tangles of reed or grass, sometimes over water.
It lays 2-4 eggs, sometimes before the nest has been completed, and are probably
incubated by the male. The chicks are fed mainly locusts and frogs by both
parents, leaving the nest after about 17 days.
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to south-central Africa, occurring in a small band
from south-western Tanzania to Angola, northern Botswana and the Caprivi Strip. It
generally prefers dense
waterside vegetation, especially in swamps, inundated flood plains and vleis.
|
 |
|
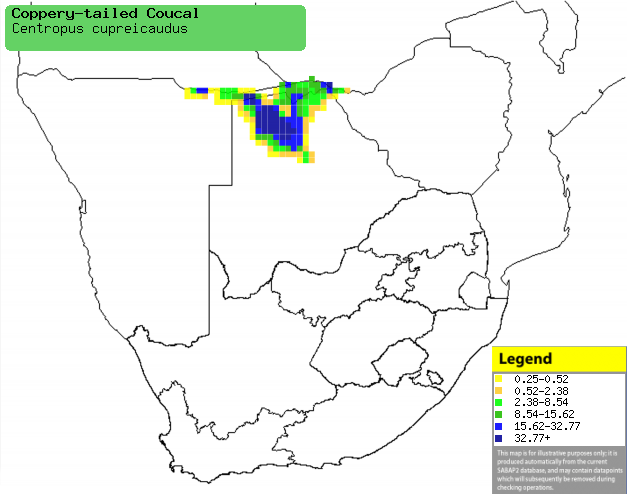
Distribution of Coppery-tailed coucal in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Food
The following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Vertebrates
- grasshoppers (Orthoptera)
- fish
- frogs
- Hyperolius (reed-frogs)
- Ptychadena (grass-frogs)
- reptiles
- birds
- rodents (Rodentia)
Breeding
- The nest is a scruffy grass platform, probably built by the male. It is usually placed in dense tangles of reed
or grass, sometimes over water.
- Egg-laying season is from January-March.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, sometimes before the nest has been completed. They are probably incubated by the male
only.
- The chicks are fed mainly locusts and frogs by both parents, leaving the
nest after about 17 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
