|
Malcorus pectoralis (Rufous-eared
warbler)
Rooioorlangstertjie [Afrikaans]; Roodoorprinia [Dutch];
Prinia à joues rousses [French]; Rotbackensänger [German];
Felosa-de-faces-ruivas [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Cisticolidae
 |
 |
 |
|
Rufous-eared warbler male, Kimberley, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Rufous-eared warbler female (top) and male
(bottom), Beaufort West, South
Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to southern Africa, with the bulk of its population
in west-central South Africa, extending into southern Namibia and Botswana. It
is especially common in the shrublands of the Karoo and Kalahari.
|
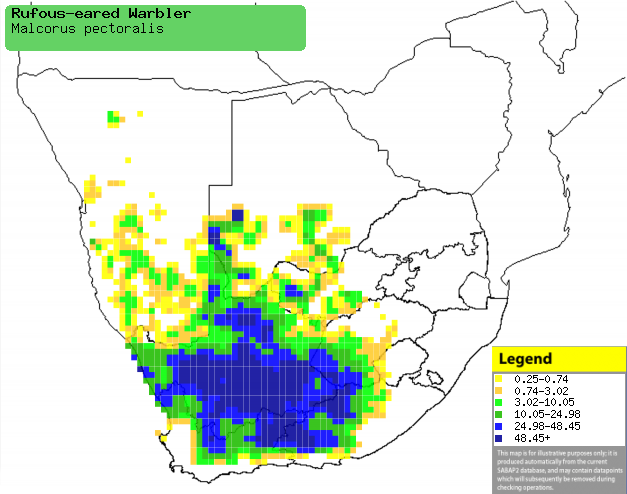 |
|
Distribution of Rufous-eared warbler in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats invertebrates supplemented with small fruit
and seeds, often gleaning prey from the stems and leaves. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Fruit
- Seeds
- Asparagus
- Lycium (honey-thorns)
- Atriplex semibaccata (Creeping saltbrush)
Breeding
- The nest is an untidy oval shape with a side-top entrance, built of grey
grass leaves and stems, or alternatively from strips of milkweed (Asclepias
buchenaviana), reinforced with spider web and lined with plant down. It
is typically placed up to 1 metre above ground in a bush or shrub, such as
Driedoring (Rhigozum trichotomum), Doringvygie (Ruschia spinosa)
and Bloubrakbossie (Galenia fruticosa).
- Egg-laying season is year round, but it generally lays its eggs after
rainfall.
- It lays 2-7, usually 2-4 eggs, which are incubated for about 12-13 days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 11-13
days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
