|
Columba delegorguei (Eastern
bronze-naped pigeon, Delegorgue's pigeon)
Withalsbosduif [Afrikaans]; Indenga [Xhosa]; iJuba
(also applied to Speckled pigeon) [Zulu]; Delegorgue-duif [Dutch]; Pigeon de
Delegorgue [French]; Bronzehalstaube, Glanznackentaube [German]; Pombo de
Delegorgue [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Columbiformes > Family:
Columbidae > Genus: Columba
 |
|
|
Eastern bronze-naped pigeon, Castle Forest Lodge,
Mt Kenya, Kenya. [photo
Megan Perkins ©] |
|
Distribution and habitat
It has two separate populations; one in Tanzania and Kenya
and the other in southern Africa. Here it is uncommon in central Mozambique and
the east of KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape. It generally prefers the canopy of
lowland and riverine forest and dense woodland, also moving into thick bush,
alien pine (Pinus) plantations and gardens.
|
 |
|
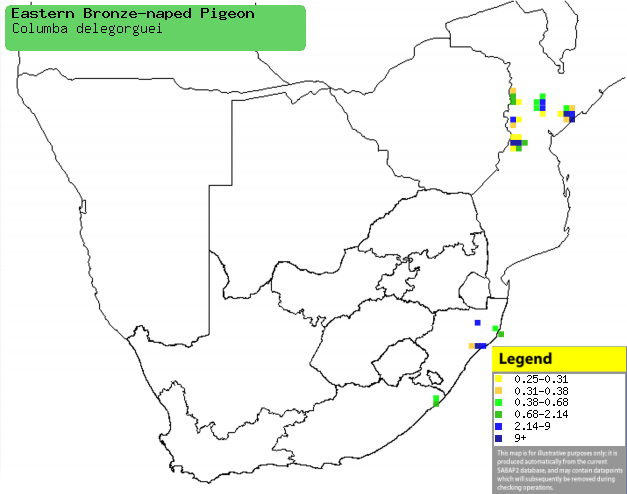
Distribution of Eastern bronze-naped pigeon in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Largely resident and locally nomadic, moving
response to the availability of fruiting trees.
Food
Mainly eats fruit, doing most foraging in the early morning
and evening in the tree canopy. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Plants
- fruit
- Podocarpus latifolius (Broad-leaved yellowwood)
- Trema orientalis (Pigeonwood)
- Macaranga capensis (River macaranga)
- Cassipourea malosana (Sand onionwood)
- Halleria lucida (Tree fuchsia)
- Helixanthera woodii (Wood's dainty mistletoe)
- Ficus (wild figs)
- Rhipsalis baccifera (Hanging wild cactus)
- Zanthoxylum davyi (Forest knobwood)
- seeds
- flowers
Breeding
- Little known in southern Africa; the female builds the nest with material
provided by the male, consisting of a flimsy platform of twigs, typically
placed in the upper branches of the tree canopy.
- Only one nest has been observed in southern Africa - in this case it
laid two eggs in December, which were incubated by both sexes.
- The chicks are fed by both parents.
Threats
Vulnerable in South Africa, as it is threatened by
the fragmentation of forests, clearing of forest patches for grazing by cattle
and the use of understorey plants for medicinal purposes.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
