|
Columba livia (Rock dove, Feral pigeon)
Tuinduif [Afrikaans];
Leeba-la-sekhooa [South Sotho]; Rotsduif [Dutch]; Pigeon biset [French];
Haustaube [German]; Pombo-doméstico [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Columbiformes > Family: Columbidae
> Genus: Columba
The Rock dove is originally native to SE Europe, SW Asia, India, Arabia, N
Africa and British Isles but is now common in many southern African cities, as
well as other cities around the world. It has been selectively bred into a wide
variety of colours, such as a mix of white, grey and fluorescent green. It feeds mainly on seeds, other plant
matter and discarded food left by humans. Both sexes build the nest, which
usually placed in buildings and bridges. It lays 1-2 eggs, which are incubated
by both sexes, for 16-19 days. In Europe, the chicks stay in the nest for 35-37
days, before fledging, at which point they become fully independent.
Distribution and habitat
Originally native to south-eastern Europe, south-western Asia, India, Arabia,
north
Africa and British Isles but it is now common in many southern African cities, as
well as other cities around the world. It lives in urban areas and parks,
railway yards, informal settlements and cultivated areas.
|
 |
|
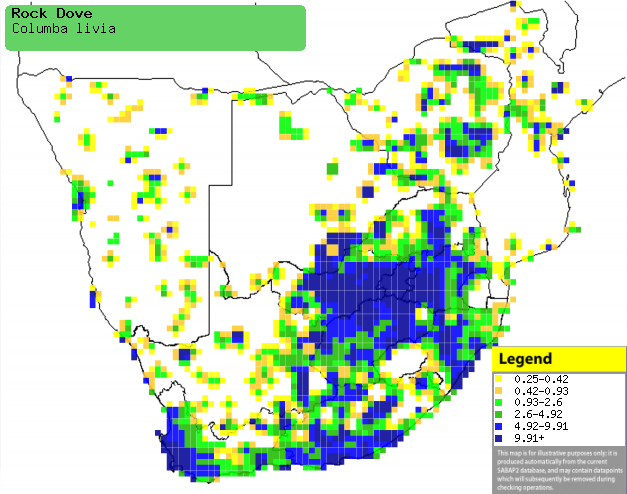
Distribution of Rock dove in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
Food
Mainly eats seeds, as well as discarded
human food and plant matter. It typically forages on open ground, such as pavements,
roads, lawns and bare soil. The following food items have been recorded in its
diet:
- Plants
- seeds
- green shoots
- berries
- leaves
- cereal plants
- Discarded human food
- Animals
Breeding
- It builds its own nest, which is a scruffy collection of twigs,
wire, feathers and other material, usually placed on ledges of buildings or
bridges.
- It can lay 1-2 eggs at any time of year.
- Incubation starts with the first laid egg, and is done by both sexes for
16-19 days.
- In Europe, the chicks stay in the nest for 35-37 days. They become fully
independent when they learn to fly.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
