|
Coccopygia quartinia
(Yellow-bellied waxbill, East African swee)
[= Estrilda quartinia]
Tropiese swie [Afrikaans]; Astrild ŕ ventre jaune
[French]; Grünastrild [German]; Bico-de-lacre-tropical [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Estrildidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in patches from Ethiopia through Kenya and Tanzania
to southern Africa, where it is locally common in Zimbabwe's eastern highlands
and adjacent Mozambique. It generally favours bracken-brier and rank vegetation
on the forest edge, pine (Pinus) plantations with dense undergrowth,
fallow fields and gardens.
|
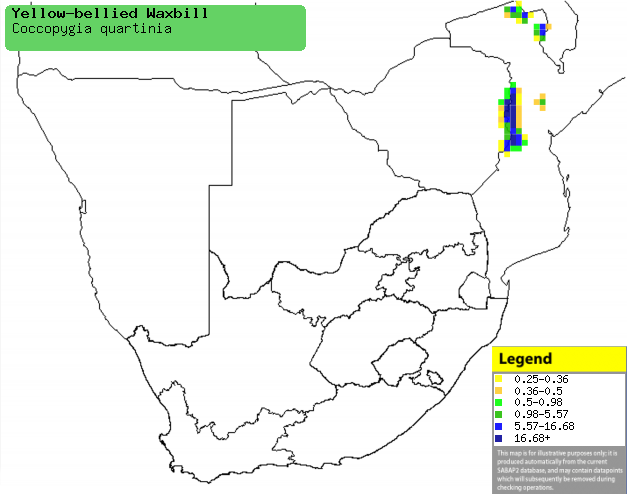 |
|
Distribution of Yellow-bellied waxbill in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Food
It mainly eats grass seeds, such as Catstail grass (Sporobolus
pyramidalis), Natal redtop (Melinis repens) and bristle grasses (Setaria),
taken from the ground or directly from plants.
Breeding
- The nest is built by both sexes in about 7-10 days, consisting of an
oval-shaped structure with a side-top entrance, made of coarse grass and
lined with soft grass inflorescences and occasionally moss. It is typically
placed in a leafy bush or tree roughly 1-5 metres above ground.
- Egg-laying season is from December-April.
- It lays 4-5 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 12-14
days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents on a diet of regurgitated seeds,
leaving the nest after about 13-16 days.
Threats
Not threatened, although in the period from 1995-2000 1526
birds were reported in the cage-bird trade, probably imported from Tanzania.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
