|
Hypargos margaritatus
(Pink-throated twinspot)
Rooskeelkolpensie [Afrikaans]; Katjikilili (applied to some
of waxbills and twinspots) [Kwangali]; Parelastrild [Dutch]; Sénégali de
Verreaux [French]; Perlastrild [German]; Pintadinho-de-peito-rosado
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Estrildidae
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to southern Africa, occurring across southern
Mozambique to Swaziland, KwaZulu-Natal and marginally in Mpumalanga, with an
isolated population in northern Limpopo Province. It generally prefers dry,
thick scrub, woodland with dense and tangled undergrowth, thickets, palm savanna
and edges of forest.
|
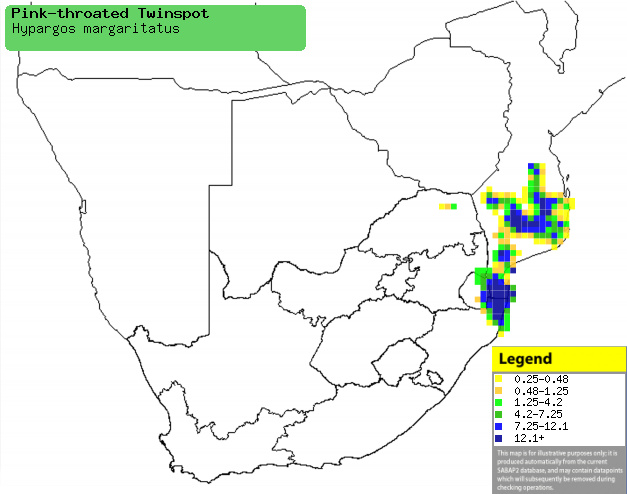 |
|
Distribution of Pink-throated waxbill in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats seeds of grasses, probably supplemented with
insects since it eats them in captivity.
Breeding
- Its breeding habits are not well known, since only two nests have been
reported in the wild.
- The nest is an untidy ball with a side entrance, made dry grass or leaf
ribs, skeletonised leaves, inflorescences and spider webs, lined with palm
fibres and leaf litter. It is typically concealed in dense vegetation and
leaf litter, less than one metre above ground.
- Only one clutch of three eggs has been recorded, laid in January,
although it can lay up to four eggs in captivity.
- In captivity the chicks stay in the nest for 20-21 days.
Threats
Not threatened globally, but Near-threatened in
South Africa and Swaziland, due to its small distribution range, habitat
destruction and the cage-bird trade, as an estimated 2000 birds are though to be
exported from Mozambique every year.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
