|
Lagonosticta nitidula (Brown
firefinch)
Bruinvuurvinkie [Afrikaans]; Bruine amarant [Dutch];
Amarante nitidule [French]; Großer pünktchenamarant [German];
Peito-de-fogo-castanho [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Estrildidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from southern DRC, Angola, Zambia and south-western
Tanzania to southern Africa, where it is locally common in northern Botswana,
north-western Zimbabwe and
north-eastern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip). It generally favours
reedbeds (Phragmites), Papyrus (Cyperus papyrus), tall grass and
thickets along watercourses, swamps and marshes, occasionally moving into
adjacent thorn scrub and riparian woodland.
|
 |
|
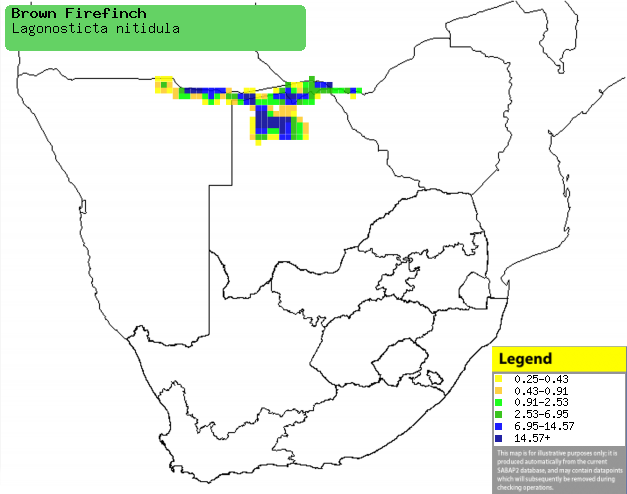
Distribution of Brown firefinch in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Predators and parasites
Its eggs are eaten by Common egg-eater (Dasypeltis
scabra).
Food
It mainly eats grass seeds supplemented with insects, doing
most of its foraging on bare ground or in cultivated areas. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Grass seeds (taken in captivity)
- Echinochloa colonum (Jungle rice)
- Eragrostis tef (Teff grass)
- Setaria verticillata (Bur bristle grass)
- Setaria sphacelata (Golden bristle grass)
- Melinis repens (Natal red top)
- Insects
Breeding
- The nest is a grass ball with a side entrance, lined with feathers and
placed low in a bush or thatch roof of a building. It may also use abandoned
nests of Spectacled weaver,
Golden weaver,
Southern brown-throated
weaver, Village weaver,
Thick-billed weaver and
sunbirds.
- Egg-laying season in Zimbabwe is from October-April, peaking from
January-April.
- It lays 3-6 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 14-16
days.
- The chicks are brooded and fed by both parents, leaving the nest after
about 15-19 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
