|
Ortygospiza atricollis (African
quailfinch, Quail finch)
Gewone kwartelvinkie [Afrikaans]; Unonkxwe [Xhosa];
iNxenge, uNonklwe [Zulu]; Mukadi gonon [Kwangali]; Lekolikotoana,
Lekolukotoana [South Sotho]; Kwartelastrild [Dutch]; Astrild-caille à
lunettes [French]; Wachtelastrild [German]; Bico-de-lacre-codorniz
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Estrildidae
 |
 |
|
African quailfinch male, Tswalu Kalahari Reserve,
South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
African quailfinch, Botswana. [photo
Neil Gray
©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in patches across sub-Saharan Africa, from Senegal
to Ethiopia south through southern DRC, Angola and Zambia to southern Africa.
Here it is locally common in South Africa, excluding most of the Northern and
Western Cape, southern Mozambique, Zimbabwe, northern and south-eastern Botswana
and northern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip). It generally favours short,
open grassland especially near water, as well as agricultural fields and
woodland with patches of bare ground.
|
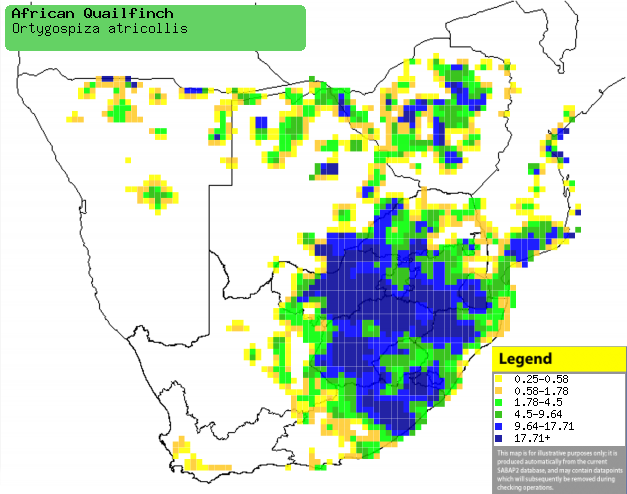 |
|
Distribution of African quailfinch in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Nomadic in the non-breeding season, moving into
regions which have recently experienced rainfall and leaving once
the ground dries up.
Food
It mainly eats grass seeds taken from the ground,
supplemented with small arthropods, especially
termites and
spiders.
Breeding
- The nest (see image below) is built by both sexes, consisting of a
ball-shaped structure of grass blades, lined with seeding grass
inflorescences and feathers. It is typically placed within or on top of a
grass tuft, with the entrance often facing a small patch of bare soil.
 |
|
|
African quailfinch nest with eggs, Sericea
farm, South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is from November-June, peaking from January-April.
- It lays 3-6 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 15 days.
- The chicks are brooded and fed by both parents, leaving the nest after
about 18-19 days and are able to fend for themselves about 26 days later.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
