|
Falco subbuteo (Eurasian hobby,
Hobby falcon)
Europese boomvalk [Afrikaans]; Kakodi (generic term for
sparrowhawks, goshawks, kestrels and falcons) [Kwangali]; Phakoe (also applied
to Lanner falcon) [South Sotho]; Rukodzi (generic name for a small raptor such
as falcon or sparrowhawk) [Shona]; Rigamani, Rikhozi (generic terms for some
falcons) [Tsonga]; Phakwę (generic term for some of the smaller raptors)
[Tswana]; Boomvalk [Dutch]; Faucon hobereau [French]; Baumfalke [German];
Ógea-europeia [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Falconiformes >
Family: Falconidae
 |
 |
|
Eurasian hobby feeding on a swift, Kruger National
Park, South Africa. [photo
Johann Grobbelaar ©] |
Eurasian hobby, Botswana. [photo
Neil Gray
©] |
Distribution and habitat
Breeds in Eurasia and north-western Africa, heading south
in the non-breeding season to southern Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, absent from
the lowland forest of the DRC and surrounding west African countries. Within
southern Africa it is scarce to fairly common in northern Namibia, Botswana,
Zimbabwe, northern and central Mozambique and eastern and southern South Africa. It generally prefers open moist woodland and forest edges, sometimes
moving into more open habitats to forage, such as coastal dunes and maccia-covered
slopes, also occupying suburban areas.
|
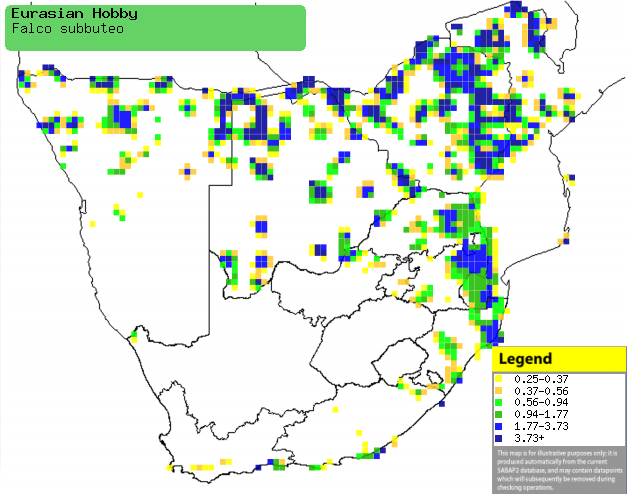 |
|
Distribution of Eurasian hobby in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Palearctic breeding migrant, leaving its
breeding grounds from August-October; it is an uncommon visitor to
southern Africa, staying from October-April.
Food
It mainly eats insects, small birds and bats, usually
hunting aerially and close to the ground; it may also spot and
seek out prey from a prominent perch. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
