|
Phedina borbonica (Mascarene
martin)
Gestreepte kransswael [Afrikaans]; Sisampamema
(generic term for swallows, martins, swifts and spinetails) [Kwangali];
Mascarenenzwaluw [Dutch]; Hirondelle des Mascareignes [French];
Maskarenenschwalbe [German]; Andorinha das Mascarenhas [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Hirundinidae
Distribution and habitat
It has two separate subspecies - one is sedentary and
occurs in Mauritius and Réunion, and the other is migratory, breeding in
Madagascar before flying to the central African coast. It is not known where its
non-breeding grounds are exactly as there are few records of it from mainland
Africa, with sightings from Kenya, Pemba Island, Malawi (in 1944 hundreds were
recorded), South Africa (specifically Crooke's Corner, Kruger National Park from
2002) and central Mozambique. Here it appeared in large numbers in from
June-July 1968 but hasn't been seen since in this country. Most southern African
records were from clearings in logged coastal Miombo (Brachystegia)
woodland.
|
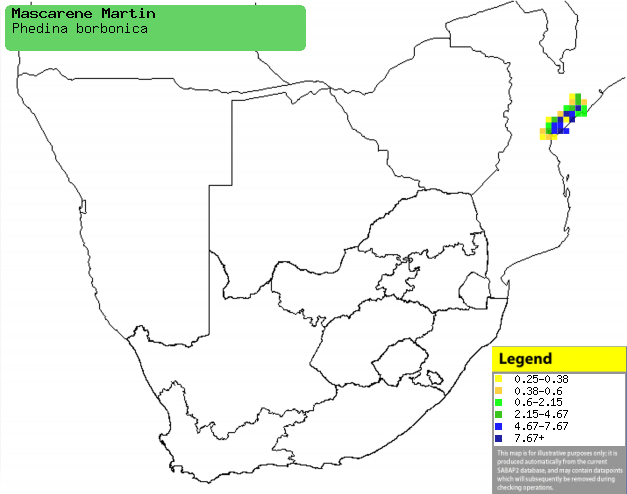 |
|
Distribution of Mascerene martin in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Movements and migrations
Non-breeding visitor to mainland Africa, with
almost all records from June-August.
Food
It eats insects, often joining mixed species foraging
flocks.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
-
Harrison, J.A., Allan, D.G., Underhill, L.G., Herremans, M.,
Tree. A.J., Parker, V. & Brown, C.J. (eds). 1997. The atlas of southern
African birds. Vol. 2: Passerines. BirdLife South Africa, Johannesburg.
|
