|
Chlidonias niger (Black
tern)
Swartmeerswael [Afrikaans]; Swartsterretjie
[Afrikaans]; Zwarte Stern [Dutch]; Guifette noire [French];
Trauerseeschwalbe [German]; Gaivina-preta [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Charadriiformes
> Family: Laridae > Genus: Chlidonias
 |
|
|
Black tern in non-breeding plumage, New Jersey,
USA. [photo Dana Beaton
©] |
|
Distribution and habitat
It has two separate populations, with one breeding in North
America before travelling to South America, while the other breeds from western
Europe to Asia, heading south in the non-breeding season to the coast and
adjacent ocean of western Africa, from Mauritania through Liberia to Cameroon,
south to southern Africa. Here it is locally common along and off the coast of
Namibia, especially near Luderitz, although it also a rare but regular visitor
to the coast of the Western Cape and KwaZulu-Natal.
|
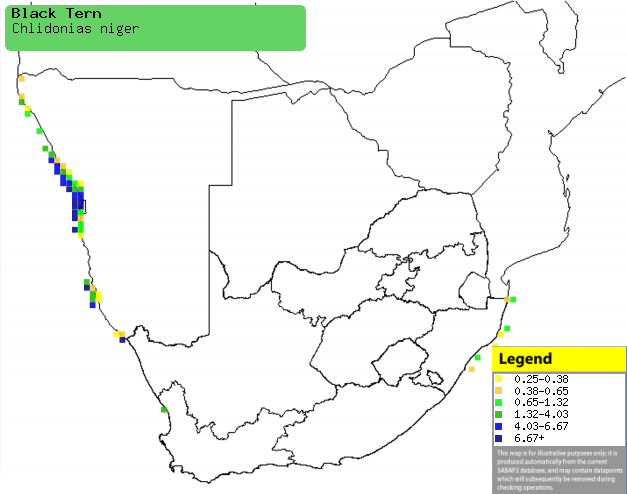 |
|
Distribution of Black tern in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Palearctic breeding migrant, mainly arriving in
southern Africa in the period from November-December, with numbers
peaking from January-February before its departure from
February-April.
Food
It mainly eats small fish, supplemented with crustaceans,
doing most of its foraging grabbing prey from the water surface. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Fish
- Crustaceans
- krill
- Macropetasma africana (Namibia surf shrimp)
- Palaemon elegans (Glass prawn)
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
