|
Larus fuscus (Lesser
black-backed gull)
Kleinswartrugmeeu [Afrikaans]; Kleine mantelmeeuw,
Baltische mantelmeeuw [Dutch]; Goéland brun [French]; Heringsmöwe
[German]; Gaivota-d'asa-escura [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Charadriiformes
> Family: Laridae > Genus: Larus
 |
 |
|
Lesser black-backed gull vagrant, Leeupan, South
Africa (recorded in August 2008). [photo
Johann Grobbelaar ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Breeds from the eastern coast of North America through
Iceland and the UK to the White Sea, heading south in the non-breeding season to
the eastern Mediterranean, the Black Sea and sub-Saharan Africa. In southern
Africa it is a sparse and erratic visitor, mainly
occurring in northern Zimbabwe and Namibia, central and southern Mozambique, the
Free State and the North-West Province. It generally prefers large lakes, pans,
dams and rivers.
|
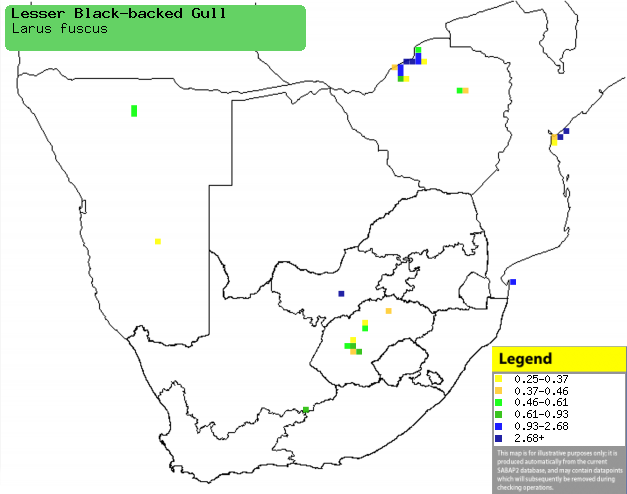 |
|
Distribution of Lesser black-headed gull in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Palearctic breeding migrant, staying for extend
periods of time in southern Africa, so arrival and departure dates
are unknown.
Food
Omnivorous, doing most of its foraging by diving into the
water to catch prey, such as the fish Kapenta (Limnothrissa miodon), or
by
hawking insects aerially.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
