|
Trachyphonus vaillantii (Crested
barbet)
Kuifkophoutkapper [Afrikaans]; iMvunduna [Zulu];
Mbangura (also generic term for woodpecker) [Kwangali]; Malioache [South Sotho];
Chizuvaguru [Shona]; Ludvonca [Swazi]; Ngoko [Tsonga]; Kôpaôpê [Tswana];
Kuifbaardvogel [Dutch]; Barbican promépic [French]; Haubenbartvogel [German];
Barbaças-de-poupa [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Piciformes >
Family: Lybiidae
The Crested barbet occurs from Angola and Zambia south to
southern Africa, where it is common in a wide range of woodland habitats. It is
omnivorous, eating largely insects when fruit is scarce, although the chicks are
fed exclusively insects. Both sexes excavate the nest, which consists of a
chamber dug into the underside of a dead branch, defended vigorously against
other hole-nesting birds. It lays 2-5, usually 3-4 eggs which are incubated by
both sexes for about 17 days. The chicks stay in the nest for about 31 days, all
the while the breeding pair enlarge the entrance hole as they grow.
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Angola and Zambia south to
southern Africa. Here it is common in Zimbabwe, Botswana, Mozambique and the
Free State Province to Limpopo Province. It prefers moist or dry open woodland,
with trees such as miombo (Brachystegia) and Mopane (Colospermum mopane).
It also occurs in suburban gardens (where it is welcome, as it feeds on snails)
and grassland with patches of alien trees.
|
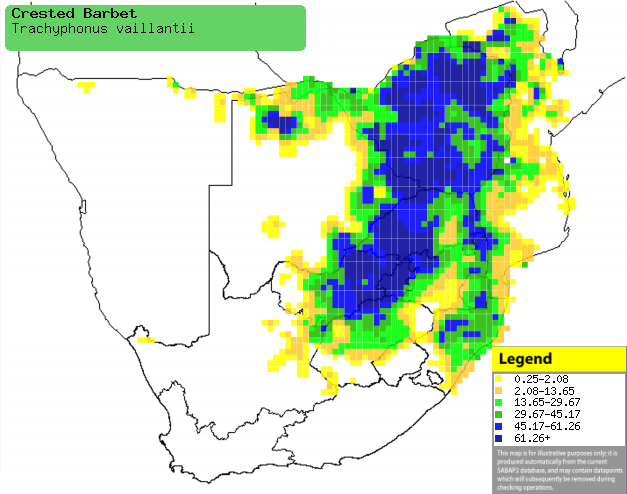 |
|
Distribution of Crested barbet in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Greater honeyguide and
Lesser honeyguide.
Food
It is omnivorous, eating largely insects
when fruit is scarce. It forages for insects mostly on the ground, sometimes
flying into foliage to eat fruit. The following food items have been recorded in
its diet:
- Animals
- invertebrates
- Occasionally, it eats eggs and chicks of other birds.
- Plants
- fruit
- Rhus (karees)
- Euclea (guarris)
- Ficus (wild figs)
- Diospyros (jackal-berries)
- nectar
-
Aloe
- Schotia brachypetala (Weeping boer-bean)
Breeding
- Both sexes excavate the nest, which consists of a
chamber dug into the underside of a dead branch. It is defended vigorously
against other hole-nesting birds, sometimes evicting enemy birds out of
their active nests!
- Egg-laying season is year-long, peaking from September-December.
- It lays 2-5, usually 3-4 eggs at 24 hour intervals.
- Incubation is done by both sexes, for about 17 days. The female
incubates during the night, with the male doing most of the day.
- The chicks are fed exclusively insects, and stay in the nest for about
31 days. The nest entrance is enlarged as they get older.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact it is common in woodland habitats.
It is a great garden bird, as it often almost eliminates the local snail population.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
