|
Prionops retzii (Retz's
helmet-shrike, Red-billed helmet-shrike)
Swarthelmlaksman [Afrikaans]; Urhiana (generic term for
helmet-shrike) [Tsonga]; Retz-klauwier [Dutch]; Bagadais de Retz [French];
Dreifarbenwürger, Dreifarb-brillenwürger [German]; Atacador-de-poupa-preta
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Malaconotidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Tanzania and Uganda through Angola to southern
Africa. Here it is fairly common in Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Limpopo Province,
KwaZulu-Natal and the Caprivi Strip. It breeds in tall deciduous woodland, such
as Miombo, Mopane and Burkea woodland, with non-breeding birds moving in to a
wider variety of habitats, including suburban gardens, Acacia savanna and
riverine forest.
|
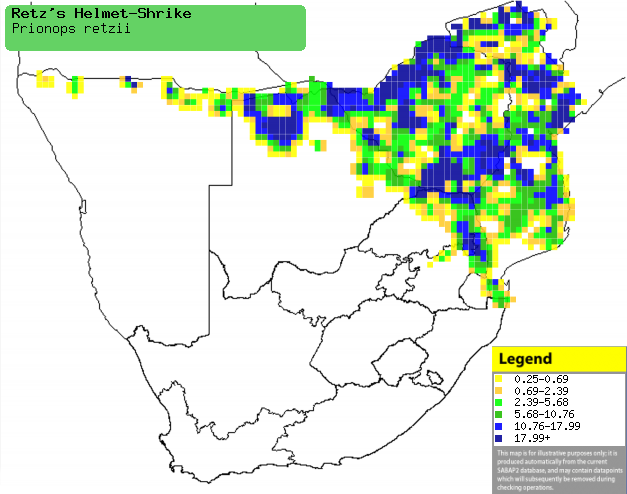 |
|
Distribution of Retz's helmet-shrike in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Thick-billed cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats invertebrates, doing most of its foraging in
the tree canopy, gleaning prey from leaves and branches. It occasionally joins
mixed species foraging flocks, along with
Chestnut-fronted and White-crested
helmet-shrikes, drongos,
orioles,
tits and woodpeckers. The following
food items have been recorded in its diet:
Breeding
- It is a monogamous cooperative breeder, meaning that the breeding pair are
helped by their siblings and/or youngsters from the previous year's breeding
season, thus forming a group. They are territorial, noisily
defending themselves against other groups and predators.
- The nest is a small cup built of bark, grass and lichen bound together
with spider web. Nest construction duties are usually shared quite equally
between the group members, although the breeding pair sometimes do more than
the others.
- Egg-laying season usually begins with the miombo (Brachystegia)
tree coming to leaf, around October-November.
- It lays 3-5 eggs, which are incubated by all group members for about
17-20 days.
- The chicks are brooded, fed and guarded by all members of the group,
changing shifts once every 11 minutes or so. The brood stay in the nest for
about 20 days, becoming fully independent about 7 months later.
Threats
Not threatened internationally, but population numbers may
be decreasing in Zimbabwe, due to the fragmentation of Miombo (Brachystegia)
woodland.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
