|
Anthus brachyurus (Short-tailed
pipit)
Kortstertkoester [Afrikaans]; Kortstaartpieper [Dutch];
Pipit cafre [French]; Kurzschwanzpieper [German]; Petinha-rabicurta
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Motacillidae > Genus: Anthus
 |
 |
| Short-tailed pipit male, KwaZulu-Natal,
South Africa. . [photo
Hugh Chittenden ©] |
Short-tailed pipit female, KwaZulu-Natal, South
Africa. . [photo
Hugh Chittenden ©] |
For information about this species, see
birdinfo.co.za.
Distribution and habitat
It mainly occurs in a teardrop-shaped area from Gabon to
Zambia, but it also has isolated populations in Tanzania, eastern DRC and
southern Africa. Here it is rare and localised, occupying the flood plains of
the Beira river in central Mozambique and small parts of KwaZulu-Natal. It
generally prefers fairly short grassland on hills, but in the non-breeding
season it may move into adjacent seasonally flooded grassland.
|
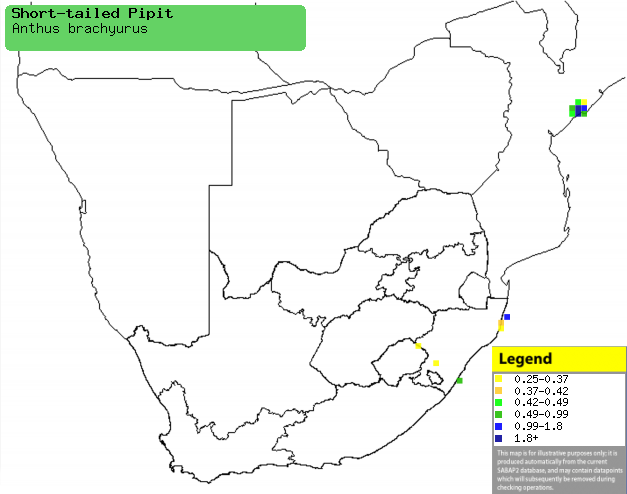 |
|
Distribution of Short-tailed pipit in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It does most of its foraging on the ground, feeding on
seeds, insects and their larvae.
Breeding
- The nest (see image below) is a small deep cup made of coarse grass and
lined with finer grass stems and rootlets. It is typically placed in a dense
clump of grass, the leaves of which conceal it from predators.
 |
|
|
Short-tailed pipit nest with chicks and egg,
KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. [photo
Hugh Chittenden ©] |
|
- It lays 2-3 eggs in the period from October-February, while egg-laying
season peaks during November.
- Little is known about the development and care of the chicks, other then
that they leave the nest after about 13 days.
Threats
Not threatened internationally but Vulnerable in
South Africa, as its favoured grassland habitat is largely unprotected and
threatened by overgrazing, coal mining and agriculture.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
