|
Macronyx croceus
(Yellow-throated longclaw)
Geelkeelkalkoentjie [Afrikaans]; iGwili, iNqomfi [Zulu];
Ligwinsi, Licomfi [Swazi]; Holiyo, Hwiyo (generic terms for longclaw)
[Tsonga]; Geelkeel-langklauw [Dutch]; Sentinelle à gorge jaune [French];
Gelbkehlgroßsporn, Safrangroßsporn [German]; Unha-longa-amarelo
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Motacillidae
> Genus: Macronyx
 |
 |
|
Yellow-throated longclaw. [photo
Jim Scarff
©] |
Yellow-throated longclaw, East Africa. [photo Jessica P. Opfer ©] |
Distribution and habitat
The most widespread of the longclaws, occurring in patches
of sub-Saharan Africa from Senegal to Uganda (absent from the DRC) south through
Tanzania and Malawi to southern Africa. Here it is locally common in eastern
Zimbabwe, Mozambique and eastern South Africa, from Limpopo province to KwaZulu-Natal,
marginally extending into the Eastern Cape. It generally prefers medium to tall grassland and the
edges of vleis, but it may move into overgrazed and burnt grassland.
|
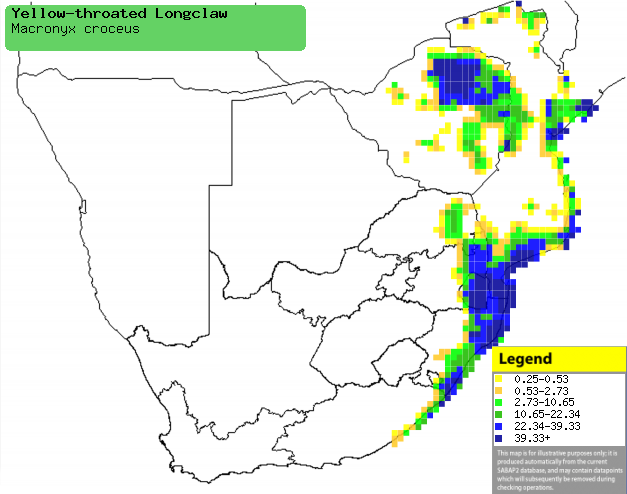 |
|
Distribution of Yellow-throated longclaw in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats insects and other invertebrates, doing most
of its foraging on the ground, plucking food from grass and occasionally hawking
prey aerially. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- Monogamous territorial solitary nester, with males performing an aerial
display in which they slowly fly in a circle with tail spread.
- The nest is built by the female, consisting of a thick-walled cup of
coarse grass blades and stems, lined with fine grass and rootlets. It is
typically concealed in rank grass, such as in the photo below.
 |
|
|
Yellow-throated longclaw at the entrance to its
nest, Eastern Shore, St Lucia,
South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is from September-March, peaking from November-January.
- It lays 1-4 eggs, which are mainly or solely incubated by the female for about
13-14 days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 16-17
days, when they are able to run fast but have yet to fly properly.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
