|
Monticola explorator (Sentinel
rock-thrush)
Langtoonkliplyster [Afrikaans]; Umganto [Xhosa]; Thume (generic
term for rock thrush) [South Sotho]; Langteen-rotslijster [Dutch];
Monticole espion [French]; Langzehenrötel [German];
Melro-das-rochas-sentinela [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Muscicapidae > Genus: Monticola
 |
 |
|
Sentinel rock-thrush male. [photo
Jeff Poklen
©] |
Sentinel rock-thrush male, Rooiels, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
 |
|
|
Sentinel rock-thrush juvenile, top of Sani Pass,
Drakensberg, South Africa-Lesotho border. [photo Alan Manson
©] |
|
For information about this species, see
www.birdforum.net/opus/Monticola_explorator Distribution and habitat
Endemic to South Africa, Swaziland and Lesotho, generally
preferring alpine grassland and heathlands on hills, felled plantations with
exposed rocks, open, boulder-strewn rangeland with grass. It also occurs in
mountain fynbos near sea level in the Western Cape, and around villages and
towns at high altitudes.
|
 |
|
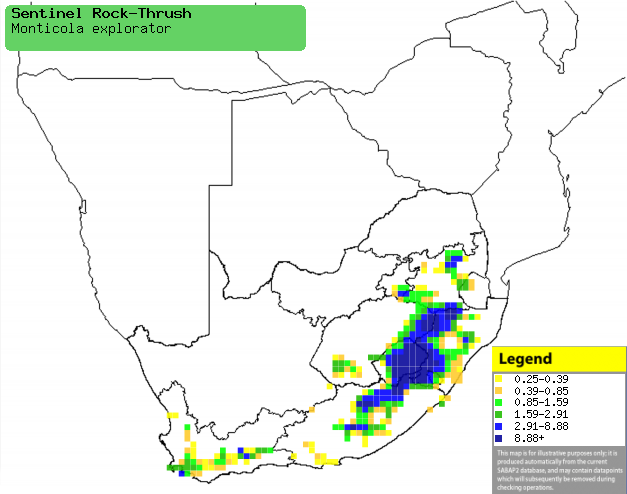
Distribution of Sentinel rock-thrush in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Mainly resident, although it may move to lower
altitudes in winter.
Food
It eats arthropods supplemented with grass and seeds, doing
most of its foraging on the ground, searching for food amongst grass tufts and
rocks. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- The nest is built solely by the female, and is a platform of grass twigs
and roots with a cup-shaped cavity set into the middle which is lined with
finer material. It is typically placed in a rock crevice, on a ledge, under
a rock or occasionally against a grass tuft on a grassy slope.
- Egg-laying season is from about September-January.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
13-15 days.
- The chicks are mainly fed by the female, leaving the nest after about
16-18 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
