|
Anthreptes reichenowi
(Plain-backed sunbird, Bluethroated sunbird)
Bloukeelsuikerbekkie [Afrikaans]; Blauwkeel-honingzuiger
[Dutch]; Souimanga de Reichenow [French]; Blaukehl-nektarvogel [German];
Beija-flor-de-garganta-azul [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Nectariniidae
 |
|
|
Plain-backed sunbird male, Arabuko-Sokoke forest,
Kenya. [photo Steve Garvie
©] |
|
Distribution and habitat
Occurs along the eastern coastal lowlands of south-central
Africa, from southern Kenya and eastern Tanzania through to parts of southern
and central Mozambique, rarely recorded in eastern Zimbabwe, Limpopo Province
and Swaziland. It generally prefers moist evergreen forest, mangroves, miombo (Brachystegia)
woodland, tall sand forest and stands of Lebombo ironwood (Androstachys
johnsonii) trees.
|
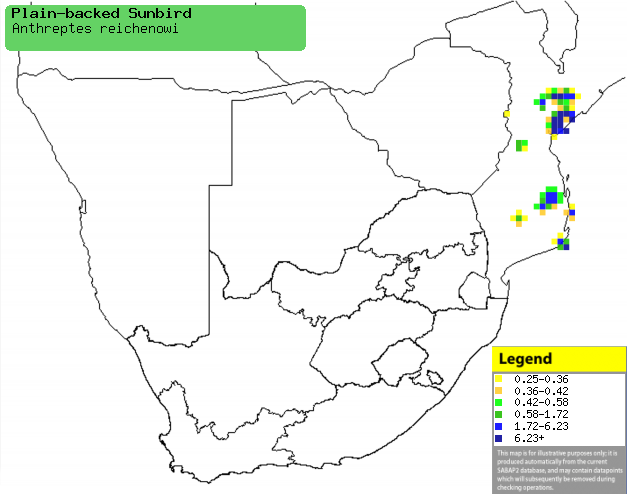 |
|
Distribution of Plain-backed sunbird in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats arthropods supplemented with nectar,
gleaning prey from leaves and often aerially hawking insects from vegetation. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Arthropods
- Nectar
- Albizia (albizias)
- Diospyros (jackal-berries)
- Mimusops (red milkwoods)
- Tapiunthus (mistletoe)
- Kigelia africana (Sausage-tree)
Breeding
- The nest is an oval-shaped structure built of shredded dry grass, twigs,
bark, leaves and lichen bound with spider web, with a side entrance covered
by a hood of grass stems. It is typically suspended from a side branch of a
liana extending across open forest.
- Egg-laying season is from June-November.
- It lays 1-3 white eggs, speckled with dull reddish brown.
Threats
Near-threatened globally and Threatened in
southern Mozambique, largely due to deforestation of indigenous forest.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
