|
Cinnyris cupreus (Copper sunbird,
Coppery sunbird)
[= Nectarinia cuprea]
Kopersuikerbekkie [Afrikaans]; Kalyambya (generic term for
sunbird) [Kwangali]; Dzonya, Tsodzo (both are generic names for sunbird)
[Shona]; Koperhoningzuiger copper [Dutch]; Souimanga cuivré [French];
Kupfernektarvogel [German]; Beija-flor-cobreado [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Nectariniidae
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in the mesic woodand of Africa south of the Sahel,
from Senegal to Ethiopia south to southern DRC, Zambia, Angola and southern
Africa. Here it is uncommon in north-eastern Zimbabwe, north-central Mozambique
and the Caprivi Strip (Namibia), generally preferring the edges of riparian
woodland and forest, especially with waterberries (Syzigium), waxberries
(Myrica), River bushwillow (Combretum erythrophyllum) and
White-stem thorn (Acacia polyacantha).
|
 |
|
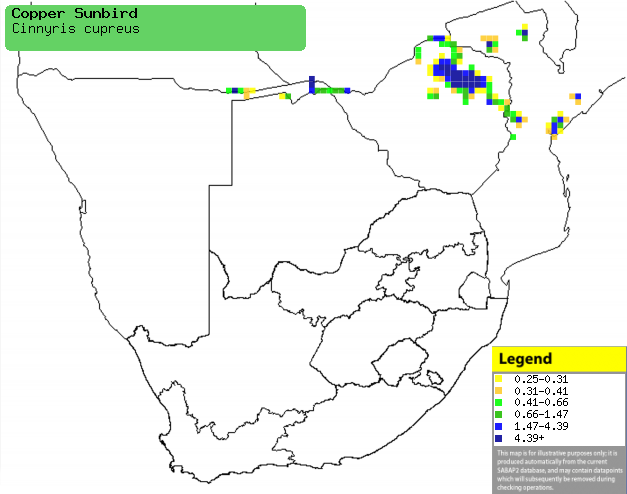
Distribution of Copper sunbird in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Predators and parasites
- Predators
- Parasites
- blood parasites
- Haemoproteus
- Plasmodium vaughani
- cestodes
- Staphylepis ambilateralis
- feather mites
- Anisodiscus dolichogaster
- Boydaia nectarinia
- Sternostoma nectarinia
Food
It mainly eats arthropods supplemented with nectar, doing
most of its foraging from a low perch, hawking prey aerially and gleaning food
from foliage. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Arthropods
- Nectar
- Leonotis (wild daggas)
- Tecoma capensis (Cape honeysuckle)
- Kniphofia (torch lilies)
- Calliandra tweedii (Mexican flame bush)
- Aloe cameronii (Cameron's ruwari aloe)
- Acrocarpus (Kenyan coffee shade trees)
- Salvia
- Bauhinia petersiana (Kalahari bauhinia)
- Combretum mossambicense (Knobbly climbing bushwillow)
- Syzigium (waterberries)
- Brachystegia spiciformis (Musasa)
- Brachystegia boehmii (Mufuti)
- Trichodesma physaloides (Chocolate bells)
- Gladiolus
- Sphenostylis marginata (Wild sweetpea)
- Tithonia rotundifolia (Red sunflower)
- Thunbergia lancifolia (Primrose)
- alien plants
- Callistemon viminalis (Bottlebrush)
- Caryopteris odorata (Verbena)
- Cuphea miniata (Summer medley)
- Jacaranda mimosifolia (Jacaranda)
- Zinnia
- peaches
- granadillas
Breeding
- The nest is built solely by the female in at least 2 weeks, consisting of
a compact oval or pear-shaped structure with an untidy base, made of dried
grass, plant stems, lichen, grass seedheads, leaf litter and plant down. The
entrance is positioned on the side, covered by a small hood about 1 cm long,
while the interior is lined with vegetable down. It is typically attached
with spider web to a twig in a bush or tree, about 0.5-3 metres above
ground.
- Egg-laying season is from December-March.
- It lays 1-2 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for at least
14 days.
- The chicks are brooded almost constantly by the female and fed by both
parents, leaving the nest after about 15-16 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
