|
Euplectes macrourus
(Yellow-mantled widowbird, Yellow-backed widow)
Geelrugflap [Afrikaans];
Geelrugwidavink [Dutch]; Euplecte à dos d'or [French]; Gelbschulterwida
[German]; Viúva-de-manto-amarelo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Ploceidae
> Genus: Euplectes
 |
|
|
Yellow-mantled widowbird, Osse River Rubber
Estate, Edo State, Nigeria. [photo
Seth of Rabi
©] |
|
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in patches across sub-Saharan Africa, from Senegal
to Ethiopia south through Angola, Tanzania and Zambia to southern Africa. Here
it is locally common in the eastern half of Zimbabwe, generally preferring moist
grassland and marshy areas, such as rank vegetation along the edges of
cultivated fields.
|
 |
|
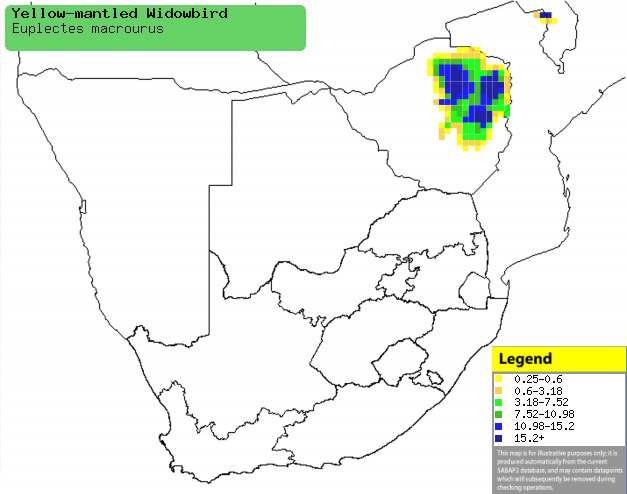
Distribution of Yellow-mantled widowbird in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Food
It mainly eats seeds (especially of sedges) taken from the
ground, supplemented with arthropods such as termite alates, hawking them
aerially from a perch.
Breeding
- Polygynous solitary nester, as males may mate with up to about 5 females
in a breeding season, vigorously defending his territory containing multiple
nests against other males and Euplectes species.
- The male can build up to about 27 nests in a breeding season, which
consist of an oval-shaped structure with a side-top entrance, made of woven
grass and lined by the female with grass inflorescences. It is typically
placed in a dense clump of grass on moist ground, the living leaves of which
are often incorporated into the nest.
- Egg-laying season is from December-March, peaking around January.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
12-14 days (recorded in captivity)
- The chicks are fed and brooded by the female only, leaving the nest
after roughly 15 days (also recorded in captivity).
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
