|
Pterocles gutturalis
(Yellow-throated sandgrouse)
Geelkeelsandpatrys [Afrikaans]; Simbote (generic term for
sandgrouse) [Kwangali]; Geelkeelzandhoen [Dutch]; Ganga à gorge jaune [French];
Gelbkehl-flughuhn [German]; Cortiçol-de-garganta-amarela [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Charadriiformes > Family: Pteroclidae
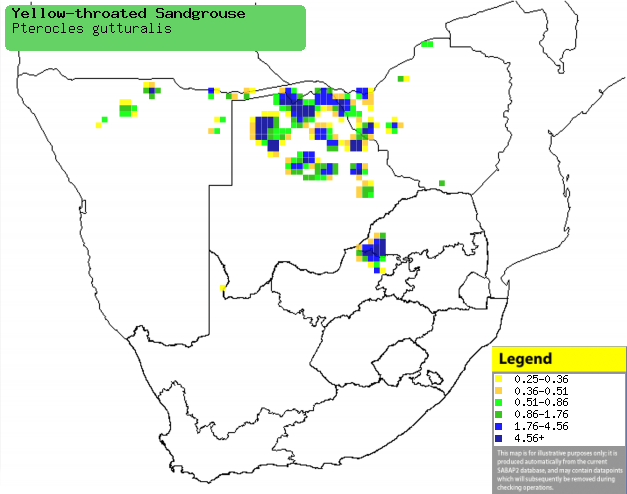
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in isolated patches of Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania,
Zambia and southern Africa, where it is generally uncommon in northern Botswana,
western Zimbabwe, south-western Limpopo Province, north-eastern North-West
Province and northern Namibia. It generally prefers short, open grassy plains
with moist clay-like soils, especially on or near seasonal rivers, swamps or
flood plains, also occupying fallow fields and cultivated land.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Yellow-throated sandgrouse in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Not well understood, although it is largely
resident in southern Africa, while a breeding visitor to southern
Zambia in the dry season.
Food
It mainly eats seeds, especially of legumes, doing most of
its foraging in flocks or pairs in the day. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- seeds
- legumes
- Crotalaria
- Cassia
- Sesbania
- Indigofera
- Amaranthus
- Achyramthes
- Bidens
- Helianthus
- Hibiscus
- Forsskaolea
- grasses
- commercial crops
- oats
- wheat
- barley
- sorghum
- soya-bean
Breeding
- Monogamous solitary nester, as nests are usually placed at least 100
metres from one another.
- The nest (see image below) is a shallow scrape in the soil, usually
lined with bits of dry grass or weed stems and typically placed beneath or
adjacent to a grass tuft or shrub.
 |
|
|
Yellow-throated sandgrouse nest with eggs, Northam
area, South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is in the dry winter months, from March-October, peaking
from April-August.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 25-26
days.
- The chicks are cared for by both parents, while the female brings them
water soaked in her belly feathers, usually fledging when they reach about a
third of their parent's size.
Threats
Not-threatened globally, but Near-threatened in
South Africa, as it is uncommon in protected areas and its largest population in
the country is spread out across fallow croplands. This means that it is
dependent on an agricultural system that leaves some of the croplands as fallow
fields, which could cause problems in the future if agricultural practices
change.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
