|
Calidris alba (Sanderling)
Drietoonstrandloper [Afrikaans]; Drieteenstrandloper
[Dutch]; Bécasseau sanderling [French]; Sanderling [German];
Pilrito-sanderlingo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Charadriiformes > Family: Scolopacidae
 |
 |
| Sanderling, California, USA. [photo
Jeff Poklen
©] |
Sanderlings foraging, California, USA. [photo Jeff Poklen
©] |
Distribution and habitat
Breeds in northern Canadian Arctic, Greenland, Siberia,
after which it disperses across the world's coasts and islands. It is common
along the entire southern African coastline, especially along the west coast,
while recorded fairly regularly in wetlands further inland. It generally prefers
sandy beaches, but it also occurs at rocky shores, lagoons and bare edges of
wetlands.
|
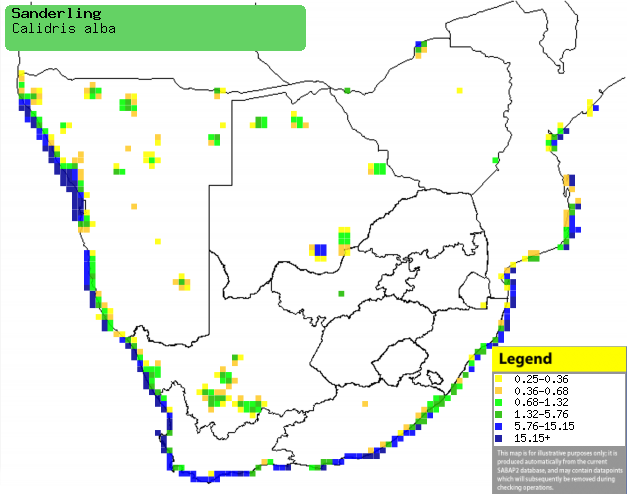 |
|
Distribution of Sanderlling in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Intercontinental migrant, with most southern
African birds arriving in small flocks from early September, all
originating from breeding grounds in Siberia and Greenland. They
eventually depart from the region in mid May.
Food
It mainly eats invertebrates, supplemented with small fish,
doing most of its foraging in flocks during the falling tide, pecking the soil
or plucking food items from rocks. It mainly forages on moist sand to avoid
confrontation with
White-fronted plovers, who often chase other birds out of their territories. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Gastrosaccus psammodytes (Surf mysids)
- Donax serra (White mussel)
- Talorchestia capensis (Beach hoppers)
- Fucellia capensis (kelp fly)
- amphipods
- isopods
- polychaetes
- mysid shrimps
- gastropods
- pycnogonids
- bivalves
- insect larvae
- mussels
- Vertebrates
- Muraenoclinnus dorsalis (Nose-stripe klipfish)
- Plants
- seeds of Zostera capensis (Cape eelgrass)
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
