|
Lamprotornis mevesii (Meves's
starling, Long-tailed starling)
Langstertglansspreeu [Afrikaans]; Ndjundju (generic term
for starling) [Kwangali]; Mwazea [Shona]; Meves-glansspreeuw [Dutch]; Choucador
de Meves [French]; Meves-glanzstar [German]; Estorninho-rabilongo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Sturnidae
> Genus: Lamprotornis
 |
 |
 |
|
Meve's starling, Kunene River Lodge, Namibia. [photo
Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Top right: Meve's starling. [photo
Neil Gray
©] Bottom right: Meve's starling, Kruger National Park, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Angola, Zambia and Malawi to southern Africa,
where it is locally common in northern Namibia, Botswana and Mozambique,
Zimbabwe and north-eastern South Africa. It generally prefers open, seasonally
flooded habitats with scattered trees such as Mopane (Colosphermum mopane),
Baobab (Adansonia digitata), Ana-tree (Faidherbia albida),
Fever-tree Acacia (Acacia xanthophloea), Umbrella thorn (Acacia
tortillis) and Leadwood (Combretum imberbe).
|
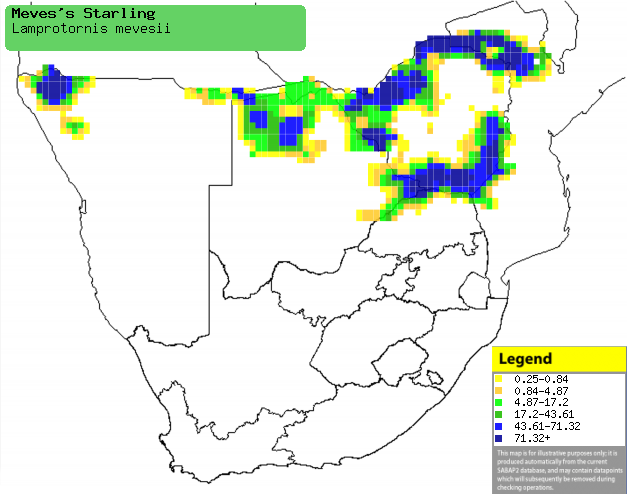 |
|
Distribution of Meve's starling in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Greater honeyguide and
Great spotted cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats insects supplemented with fruit and flowers,
doing most of its foraging on the ground, often catching prey disturbed by large
mammals such as African elephant (Loxodonta africana). The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Insects
- Fruit and flowers
- Faidherbia albida (Ana-tree)
- Diospyros mespiliformis (Jackal-berry)
Breeding
- The nest is built by both sexes, consisting of a cup built of dead plant
material typically placed in a tree cavity about 1-4 metres above ground. It
may also fence posts and ventilation pipes, often reusing the same nest over
multiple breeding seasons.
- Egg-laying season is from November-April.
- It lays 3-5 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female in about 18
days (recorded in captivity).
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 23 days
(also recorded in captivity).
Threats
Not threatened, although destruction of trees caused by
African elephants (Loxodonta africana) is cause for concern, as
they are used as nest sites.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
