|
Ammomanopsis grayi (Gray's lark)
[= Ammomanes grayi]
Namiblewerik [Afrikaans]; Namibleeuwerik [Dutch]; Ammomane de Gray
[French]; Namiblerche [German]; Cotovia da Namíbia [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Alaudidae
Distribution and habitat
Near-endemic to Namibia's Namib Desert, which marginally
extends into south-western Angola. It generally prefers open gravel plains with
or sometimes without scattered small shrubs and grass; it avoids coastal dunes
and sand desert.
|
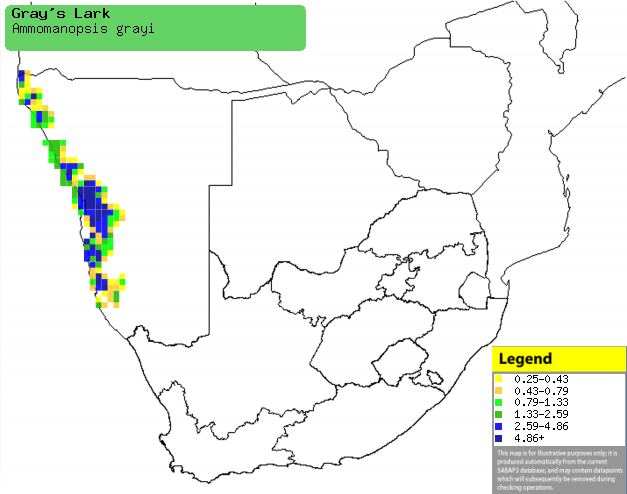 |
|
Distribution of Gray's lark in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of the following falcons:
Food
It eats seeds, invertebrates and the soft bases of grass
stems, plucking food items from the ground. It often forages around zebra and
antelope droppings and around the entrances of rodent burrows. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Seeds
- Grasses
- Forbs
- Amaranthus
- Cleon
- Giseckia
- Monsonia umbellata (Wilderabassam)
- Bases of grass stems
- Invertebrates
Breeding
- It is usually monogamous, although there have been 3 records of more than
two birds feeding fledglings, suggesting that it is an occasional
cooperative breeder.
- The nest is a thick-walled cup built of fine grass inflorescences, often
from Stipagrostis species. It is typically placed in a shallow hole
in the ground, often in the shadow of a rock, grass tuft or shrub.
- The eggs are usually laid after rainfall in them months from March-July.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated for 12-13 days; the incubating
bird is well camouflaged against the grey-coloured gravel surrounding the
nest.
- The chicks are fed invertebrates by both parents leaving the nest after
roughly 10 days, before being able to fly.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
